Standard Dataset of Lyman-Alpha Solar Flare Events
-
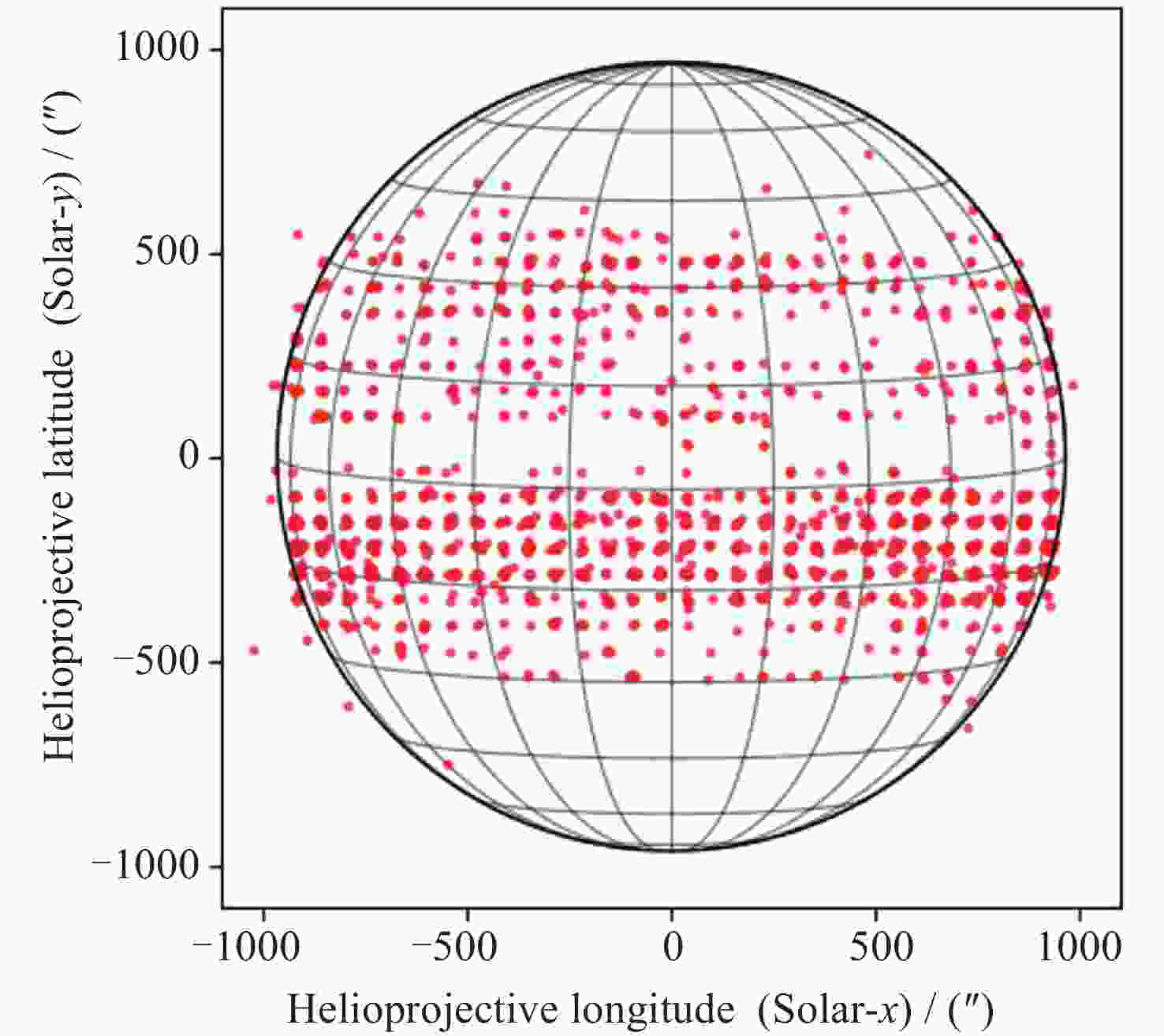
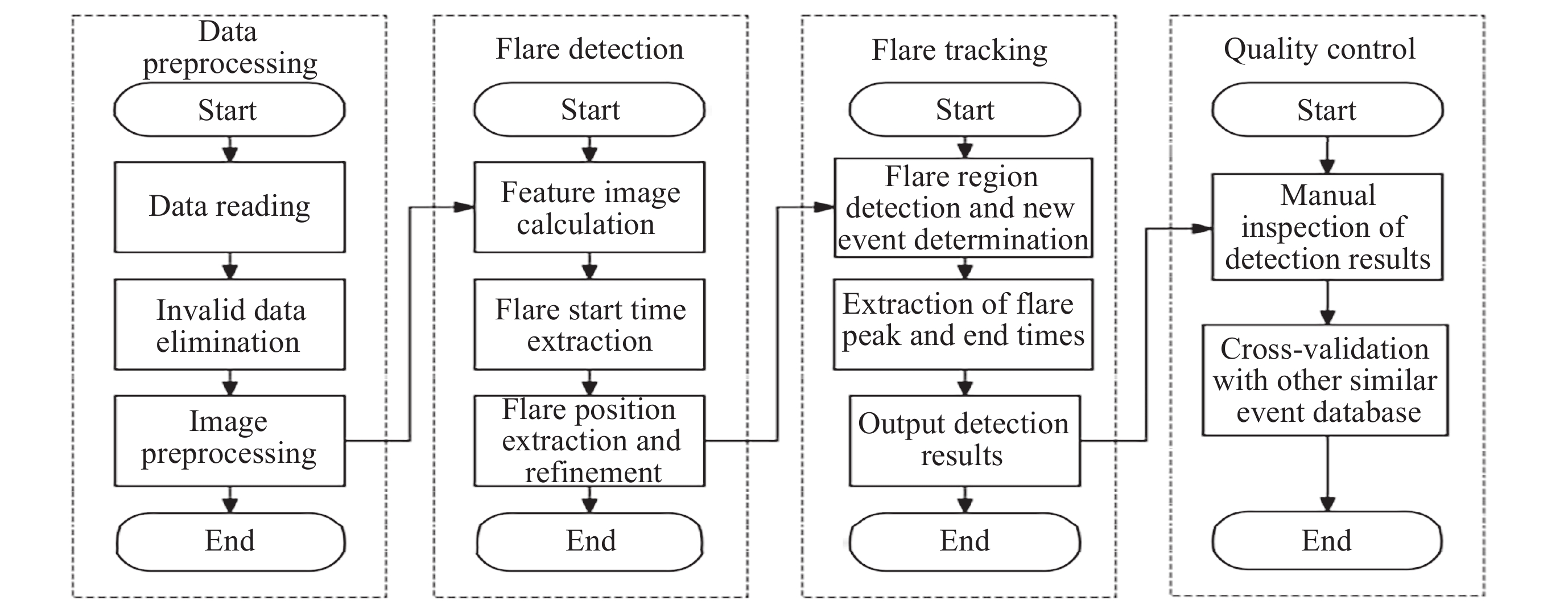
摘要: 太阳耀斑是太阳大气中最强烈的爆发现象, 能够释放大量能量并产生各种波长的电磁辐射. 研究太阳耀斑对于理解太阳活动、空间天气预报以及保护地球空间环境至关重要. 本数据集基于夸父一号(ASO-S)卫星搭载的全日面成像仪(Solar Disk Imager, SDI)在莱曼阿尔法波段(121.6±7.5) nm采集的全日面图像数据, 通过一套自主研发的太阳耀斑自动识别与关键参数提取算法, 系统记录了2024年莱曼阿尔法太阳耀斑事件. 该算法可有效避免宇宙线、粒子暴等事件的干扰, 能够对不同强度级别的耀斑进行识别, 并能对日面上同时发生的多个耀斑进行分别识别与追踪. 本数据集收录了耀斑的起止时间、持续时间、发生位置、显著性等关键参数, 包含耀斑识别过程记录文档、耀斑事件列表、耀斑峰值时刻快视图像和耀斑区域电影动画等数据. 该数据集可为太阳物理学研究、空间天气预报以及相关领域提供重要的科学数据支持.Abstract: Solar flares are the most intense eruptive phenomena in the solar atmosphere, releasing large amounts of energy and producing electromagnetic radiation across various wavelengths. Research on solar flares is crucial for understanding solar activity, space weather forecasting, and protecting the Earth’s space environment. Based on the full-disk solar images in the Lyman-alpha waveband (121.6±7.5) nm collected by the Solar Disk Imager (SDI) carried by the China’s ASO-S satellite, this dataset systematically records solar flare events observed in the Lyman-alpha band throughout 2024 using an independently developed automatic solar flare identification and key parameter extraction algorithm. This algorithm effectively avoids interference from cosmic rays and particle storms, identifies flares of different intensity levels, and can separately identify and track multiple flares occurring simultaneously on the solar disk. The dataset includes key parameters such as flare start and end times, duration, location, and significance, and contains data products including flare identification process documentation, flare event lists, quick-view images of flares at peak moments, and movies of flare regions. This dataset provides important scientific data support for solar physics research, space weather forecasting, and related fields.
-
Key words:
- Solar flares /
- Lyman-Alpha /
- Space weather /
- Automatic identification
-
表 1 Lyα太阳耀斑分类
Table 1. Classification of Lyα solar flares
强度级别 显著性特征 划分依据 微弱耀斑 S ≤ 10% Lyα辐射增强幅度不超过10%, 通常为局部小尺度能量释放 中等耀斑 10% <S ≤ 20% Lyα辐射增强幅度介于10%~20%之间, 伴有明显的亮带结构 强烈耀斑 20% < S ≤ 50% Lyα辐射增强幅度介于20%~50%之间, 通常伴有明显的色球蒸发和
能量释放极强耀斑 S > 50% Lyα辐射增强幅度超过50%, 往往伴随日冕物质抛射等大尺度爆发现象 注 S 为耀斑显著性参数, 定义为耀斑区域在Lyα波段的峰值辐射强度与背景辐射强度 (在耀斑爆发前, 耀斑所在区域的本地太阳辐射强度) 的比值减1. 表 2 Lyα太阳耀斑事件属性说明
Table 2. Description of Lyα solar flare event
属性名称 数据类型 属性说明 Date 日期型 耀斑发生日期 Start_Time 日期时间型 耀斑起始时间 (UTC) Peak_Time 日期时间型 耀斑峰值时间 (UTC) End_Time 日期时间型 耀斑结束时间 (UTC) Duration 数值型 (min) 耀斑持续时间 Position 数值型 ('') 耀斑中心坐标 (日心坐标) Peak_Flux 字符型 (DN) 耀斑峰值流量 Significance 数值型 耀斑显著性参数 表 3 Lyα太阳耀斑事件统计
Table 3. Statistics of Lyα solar flares
序号 强度级别 事件数量 数量占比/(%) 1 微弱耀斑 1337 69.0 2 中等耀斑 396 20.5 3 强烈耀斑 169 8.7 4 极强耀斑 35 1.8 合计 - 1937 100 -
[1] BENZ A O. Flare observations[J]. Living Reviews in Solar Physics, 2008, 5(1): 1 doi: 10.12942/lrsp-2008-1 [2] CURTO J J. Geomagnetic solar flare effects: a review[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2020, 10: 27 doi: 10.1051/swsc/2020027 [3] WAUTERS L, DOMINIQUE M, MILLIGAN R, et al. Observation of a flare and filament eruption in Lyman-α on 8 September 2011 by the PRoject for OnBoard Autonomy/Large Yield Radiometer (PROBA2/LYRA)[J]. Solar Physics, 2022, 297(3): 1-12 doi: 10.1007/s11207-022-01963-0 [4] GAN W Q, FENG L, SU Y. A Chinese solar observatory in space[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2022, 6(1): 165 doi: 10.1038/s41550-021-01593-9 [5] FERNANDEZ BORDA R A, MININNI P D, MANDRINI C H, et al. Automatic solar flare detection using neural network techniques[J]. Solar Physics, 2002, 206(2): 347-357 doi: 10.1023/A:1015043621346 [6] BONTE K, BERGHMANS D, DE GROOF A, et al. SoFAST: automated flare detection with the PROBA2/SWAP EUV imager[J]. Solar Physics, 2013, 286(1): 185-199 doi: 10.1007/s11207-012-0165-8 [7] LU L, TIAN Z Y, FENG L, et al. Automatic solar flare detection using the solar disk imager onboard the ASO-S mission[J]. Solar Physics, 2024, 299(5): 72 doi: 10.1007/s11207-024-02310-1 [8] LI H, CHEN B, FENG L, et al. The Lyman-alpha Solar Telescope (LST) for the ASO-S mission–I. scientific objectives and overview[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2019, 19(11): 158 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/19/11/158 [9] CHEN B, LI H, SONG K F, et al. The Lyman-alpha Solar Telescope (LST) for the ASO-S mission–II. design of LST[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2019, 19(11): 159 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/19/11/159 [10] FENG L, LI H, CHEN B, et al. The Lyman-alpha Solar Telescope (LST) for the ASO-S mission–III. data and potential diagnostics[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2019, 19(11): 162 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/19/11/162 [11] HUANG Y, LI Y P, LIU S, et al. Science operation and data analysis center of the Advanced Space-based Solar Observatory (ASO-S) mission[J]. Solar Physics, 2024, 299(9): 1-10 doi: 10.1007/s11207-024-02368-x -
-






 下载:
下载: