Research on the Performance of Beidou-3 Broadcast Ephemeris and Ionospheric Model from 2020 to 2025
-
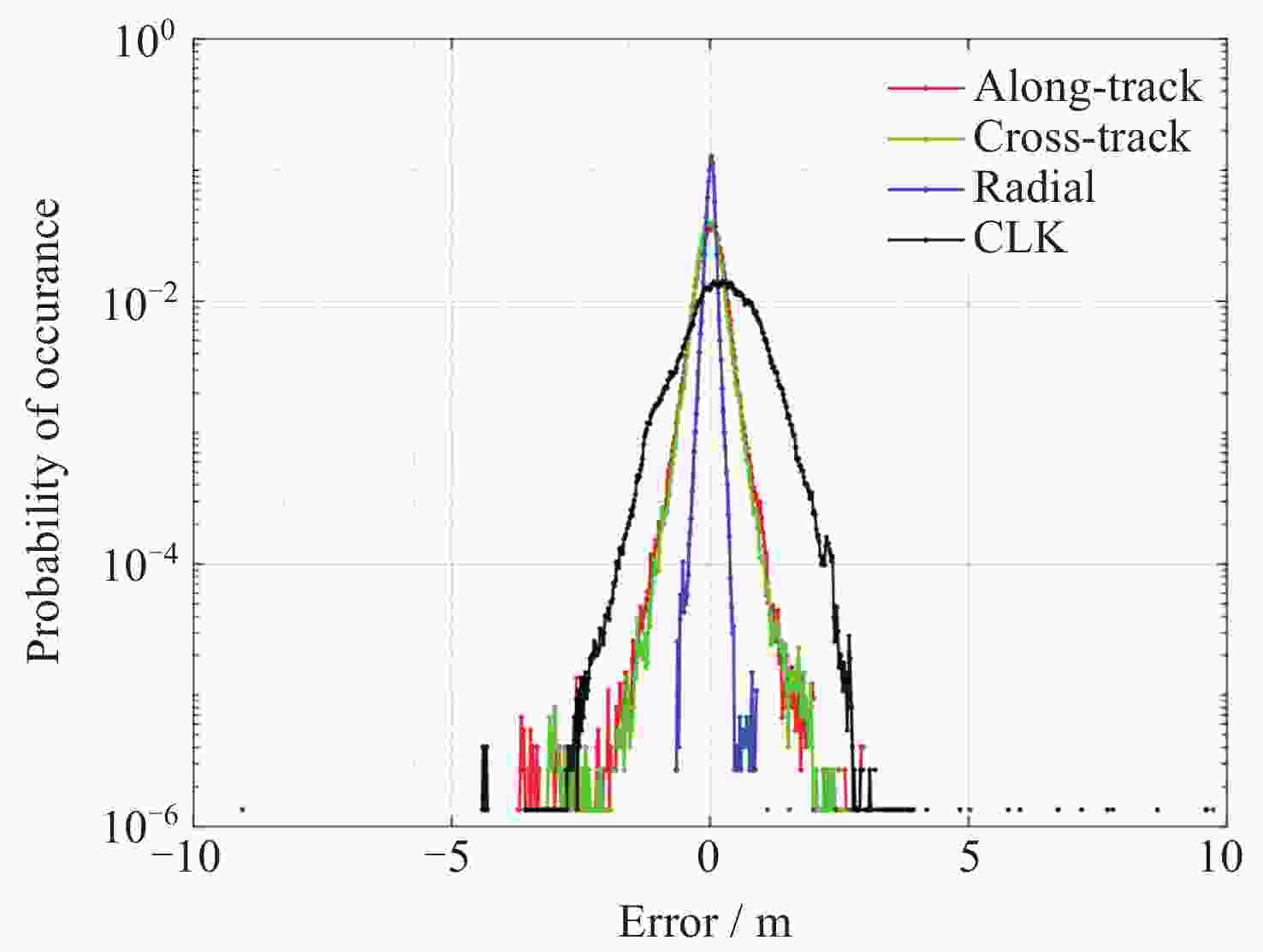
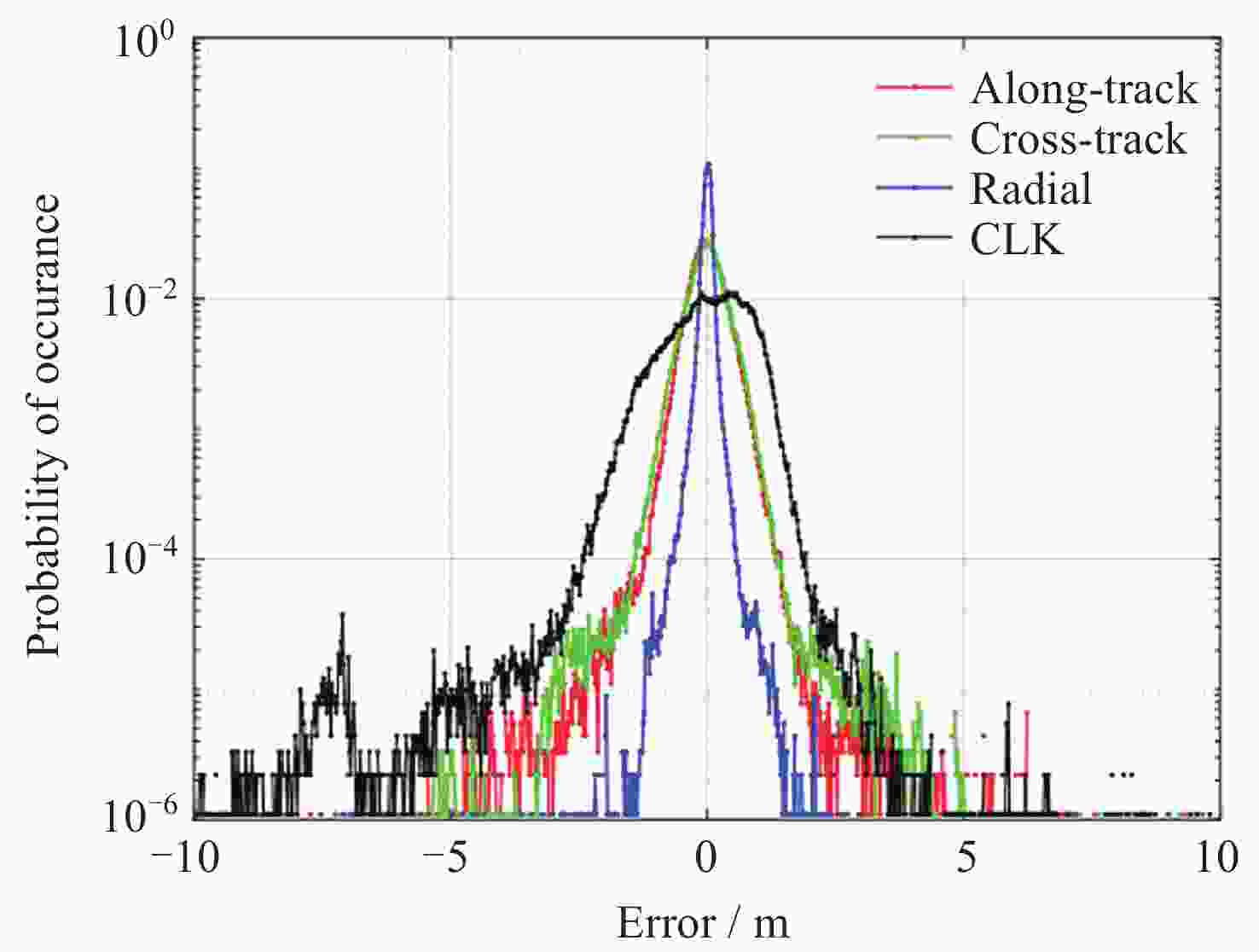
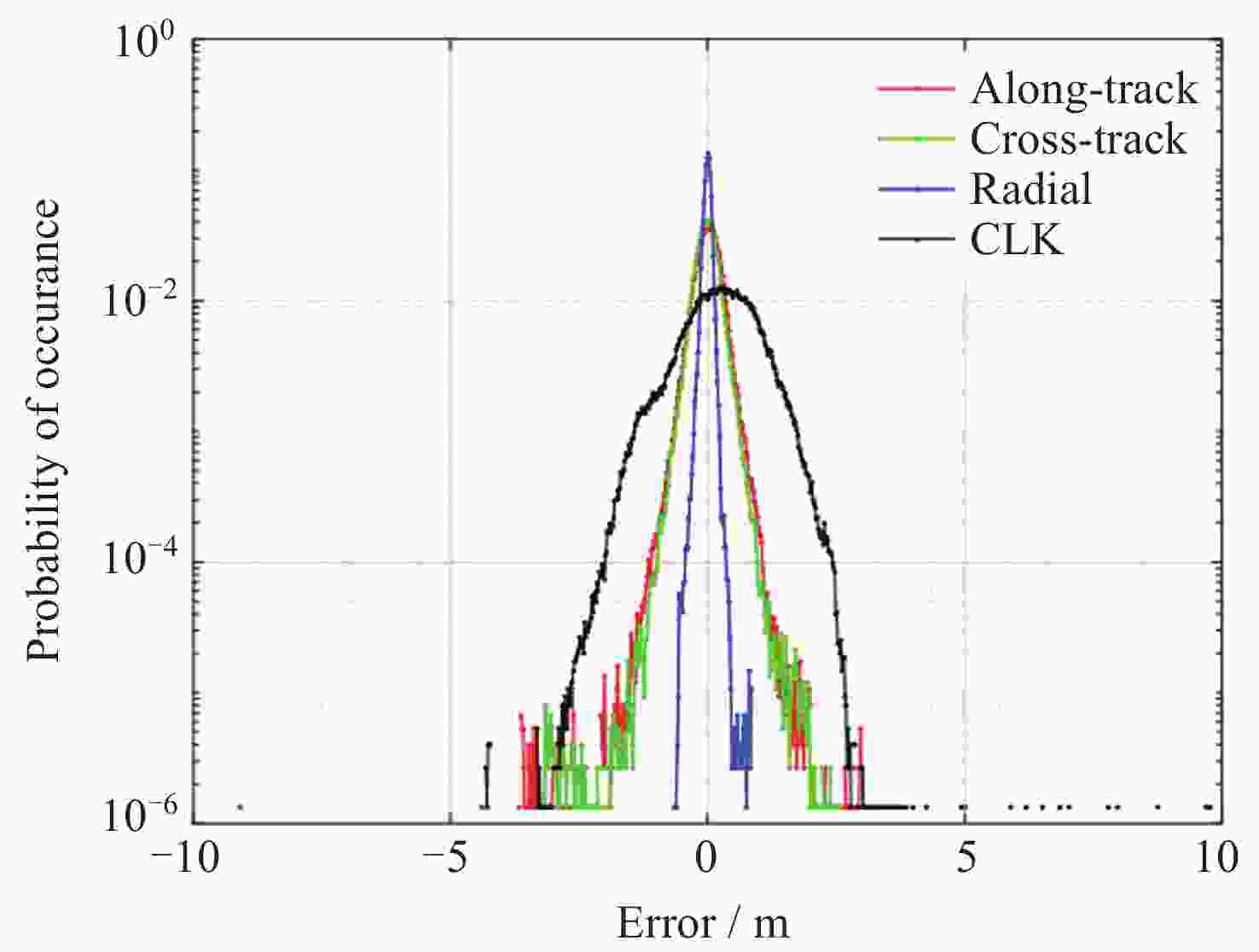
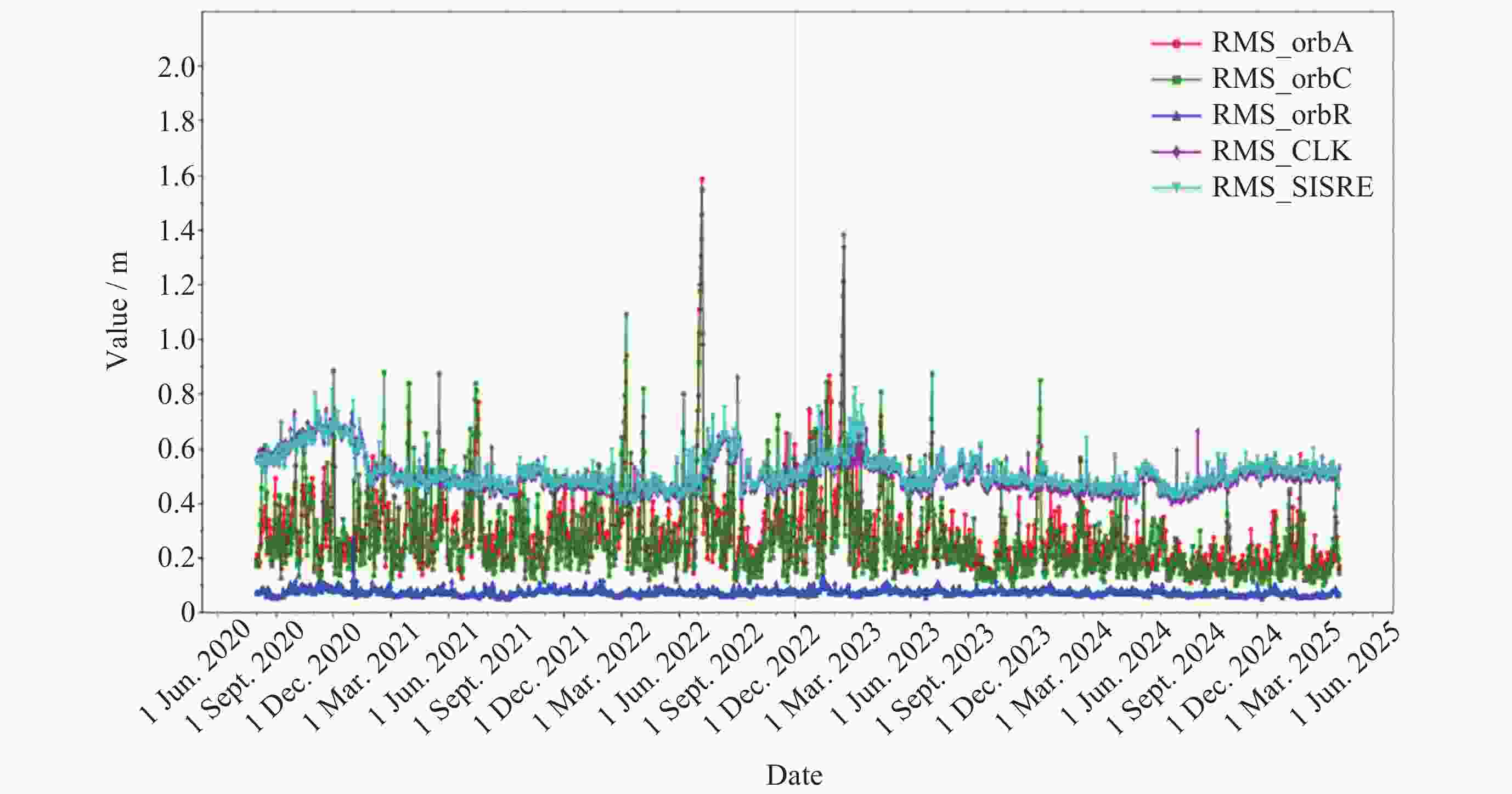
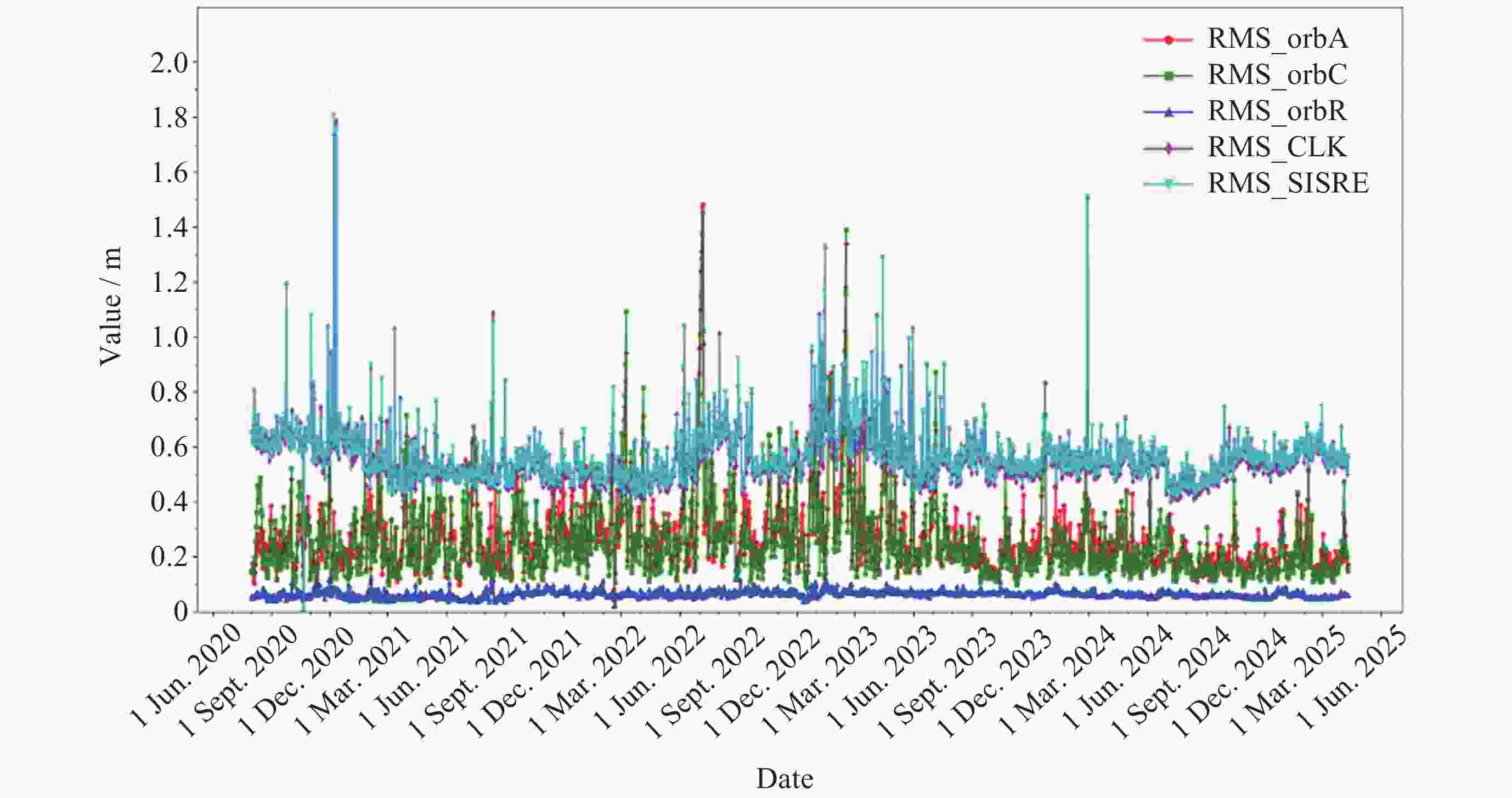
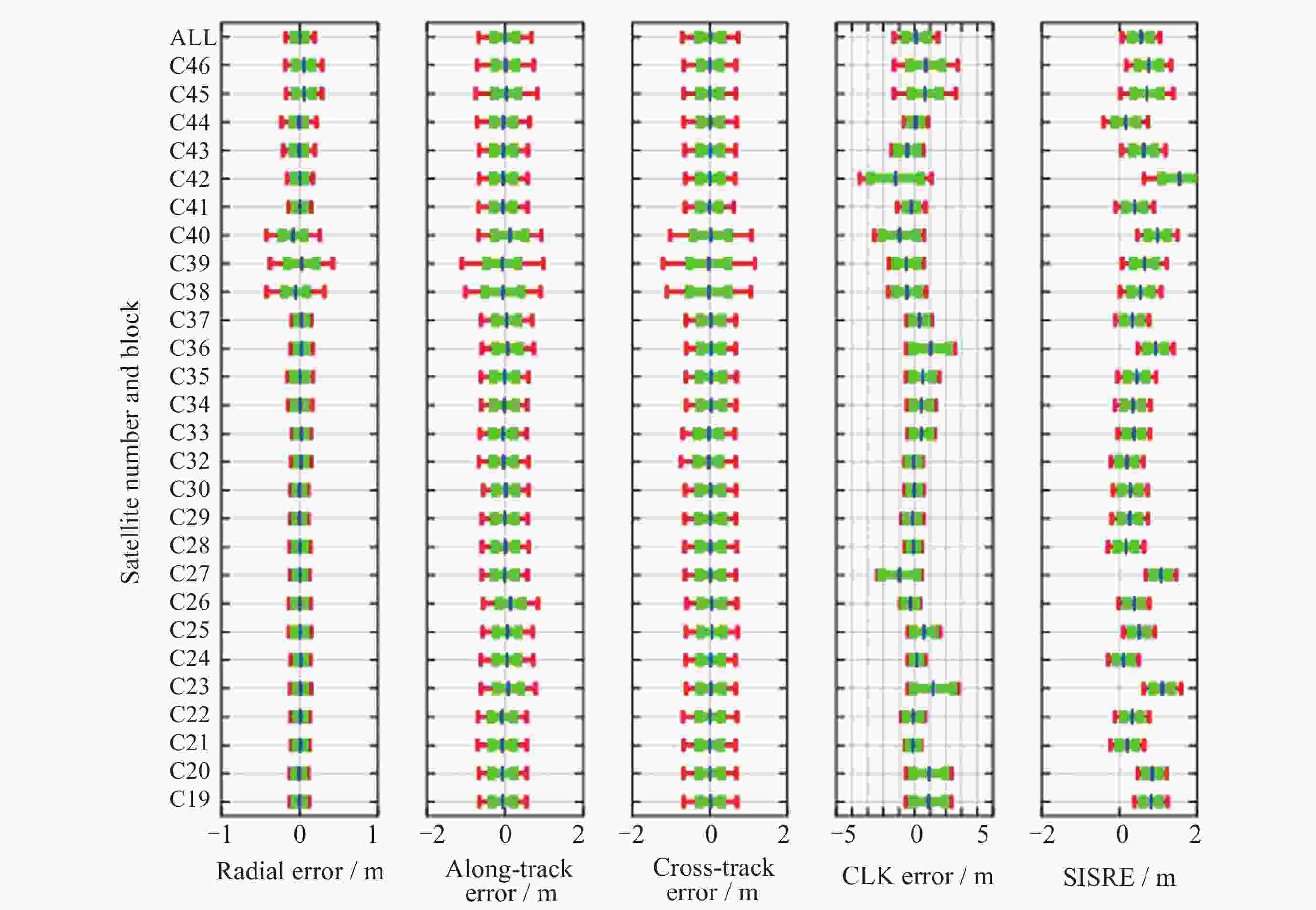
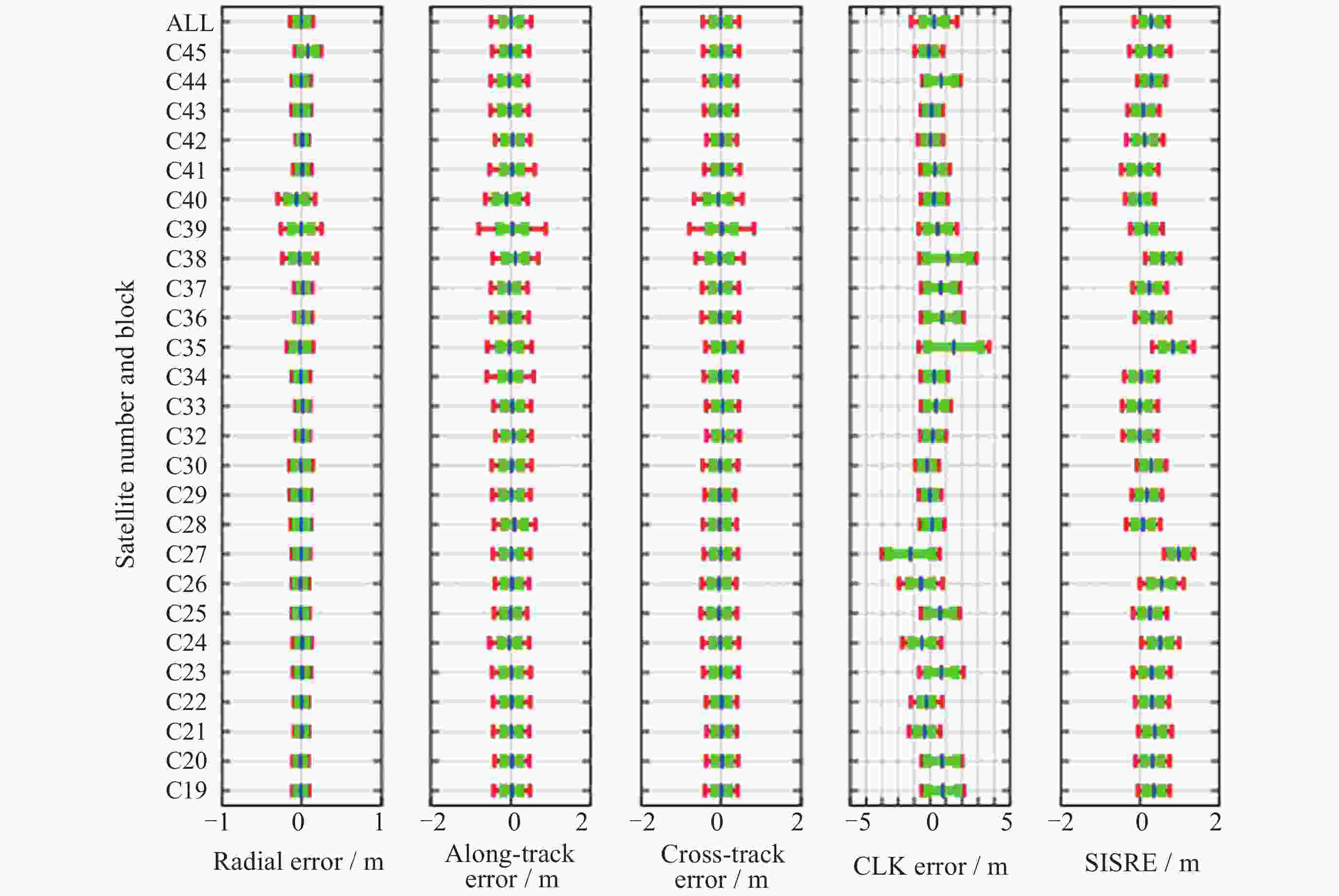
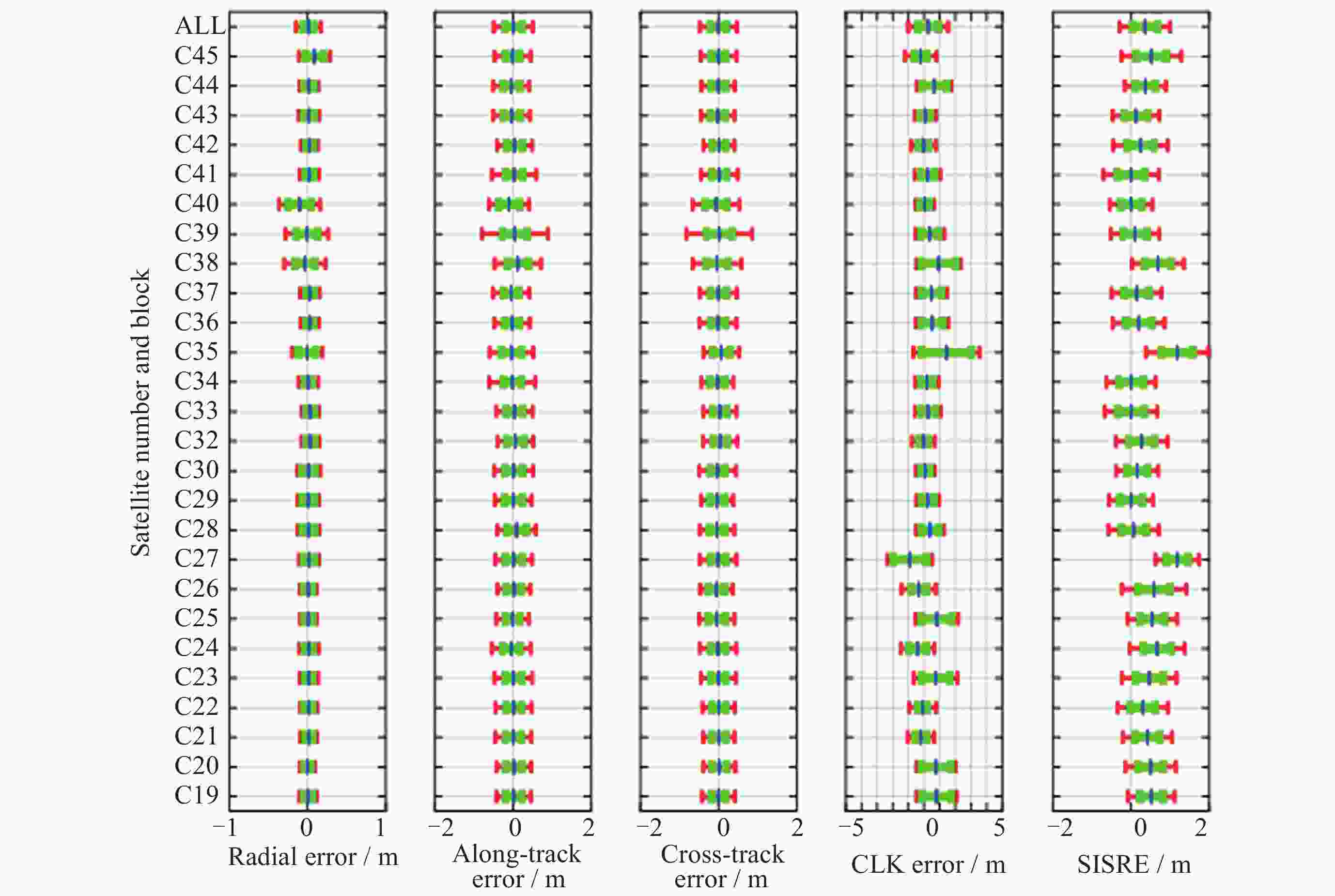
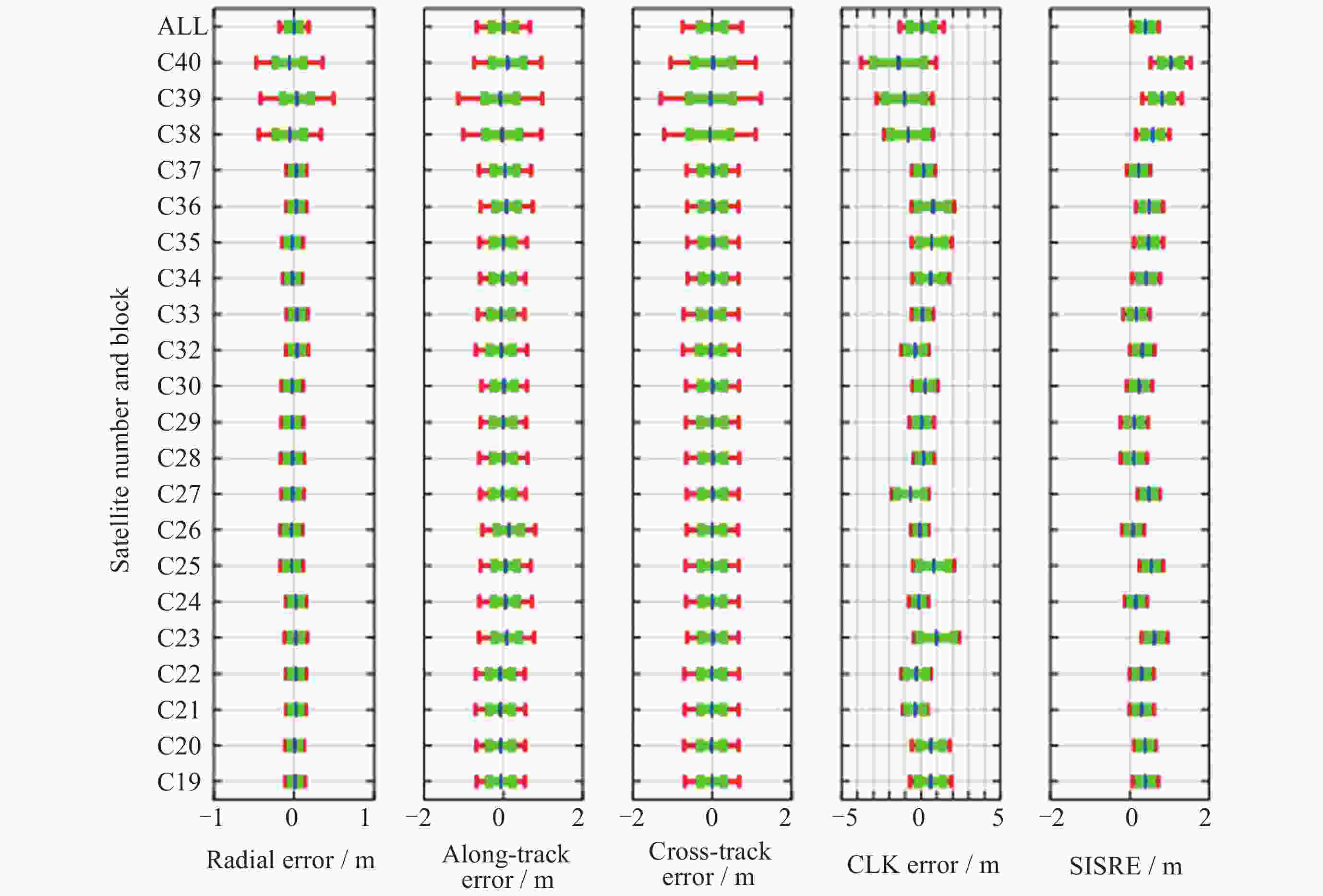
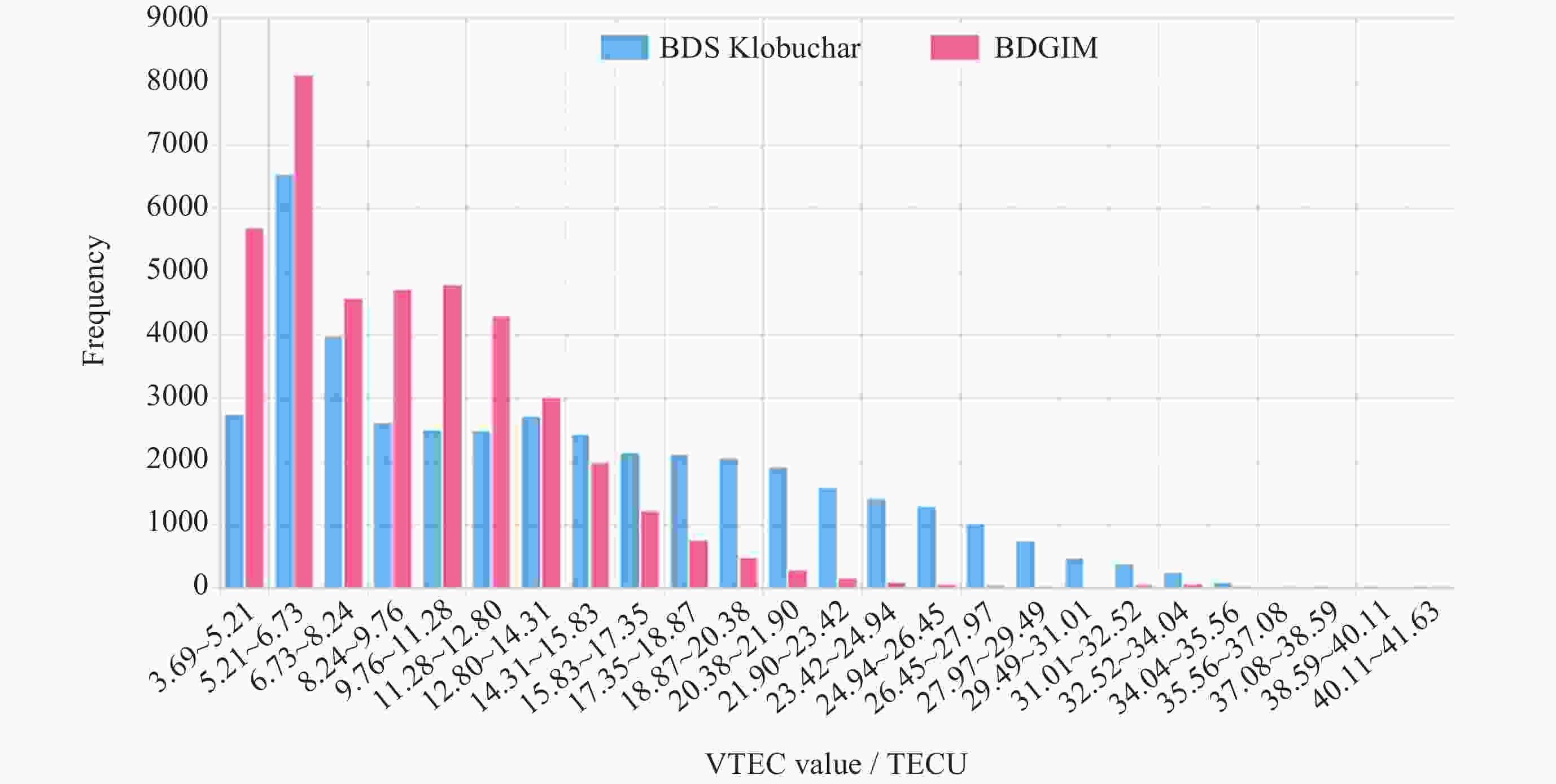
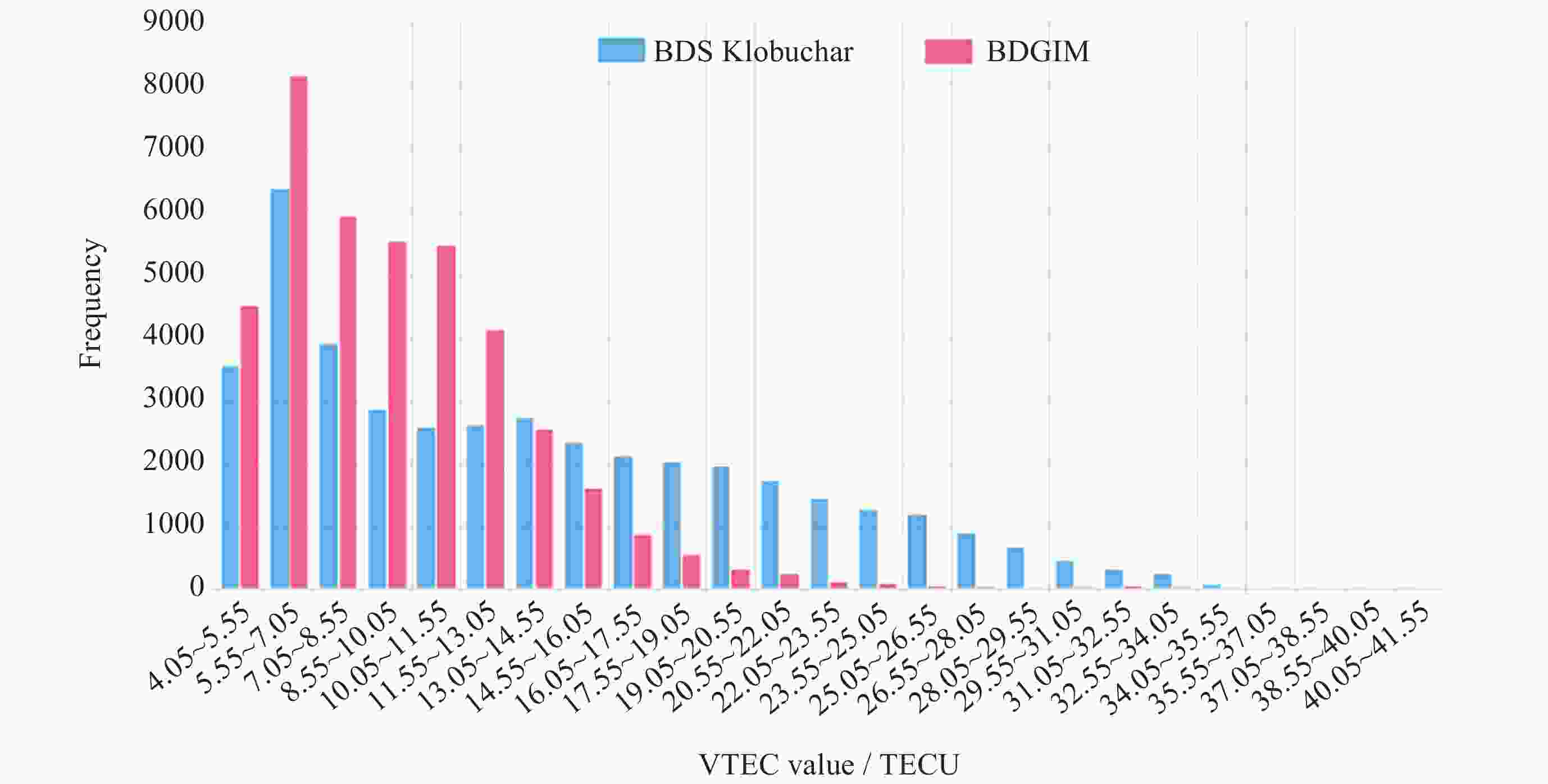
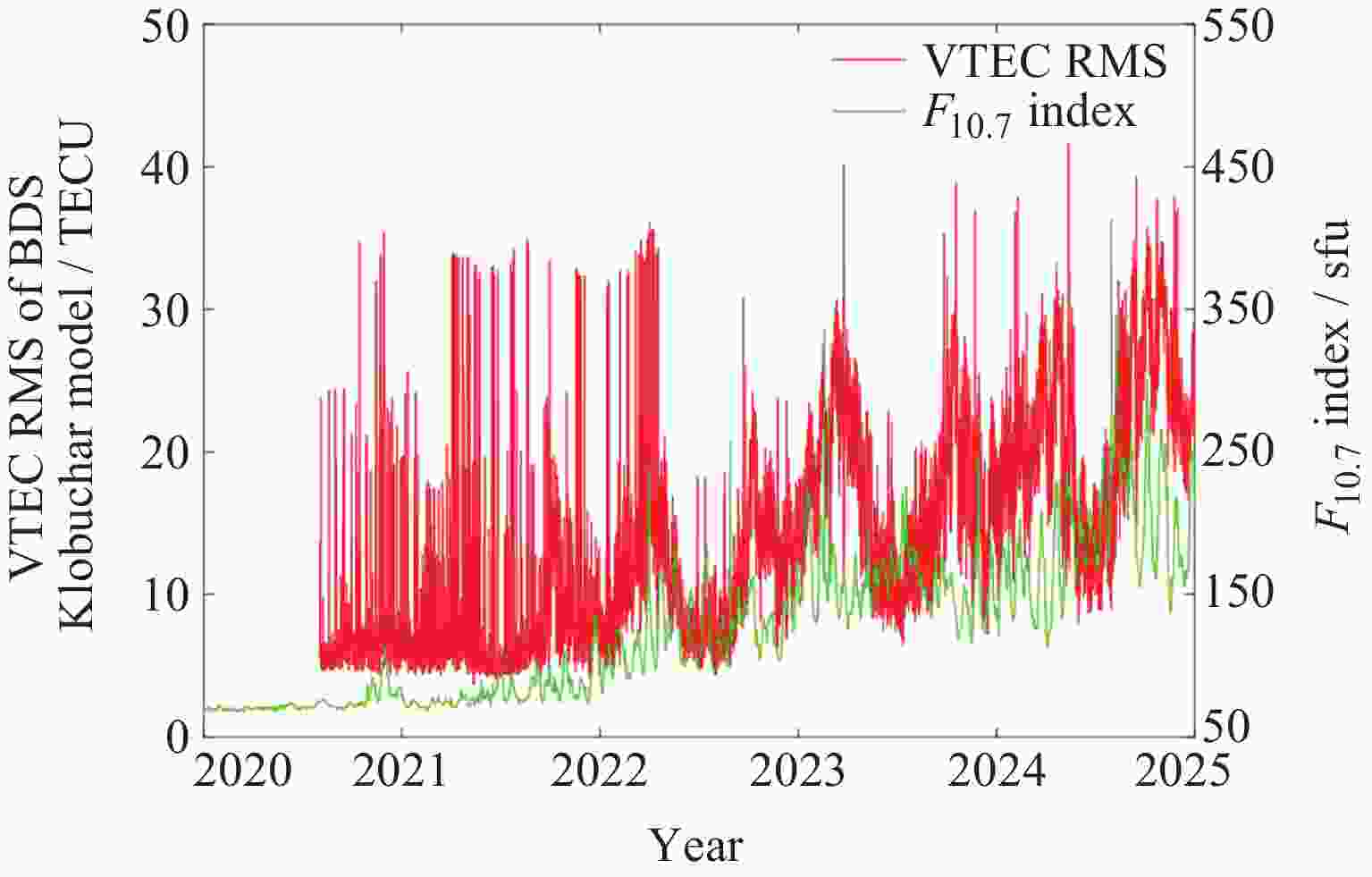
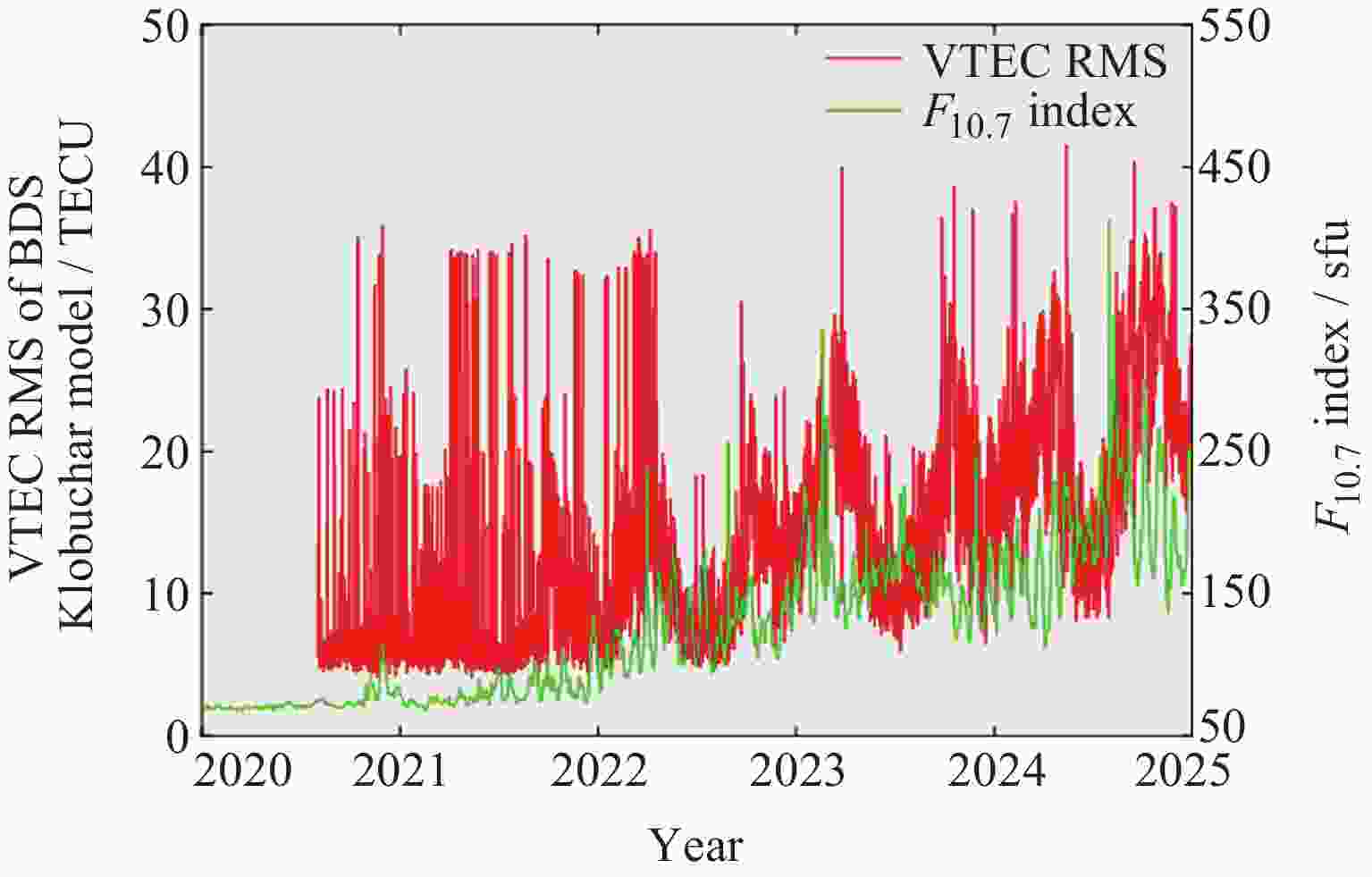
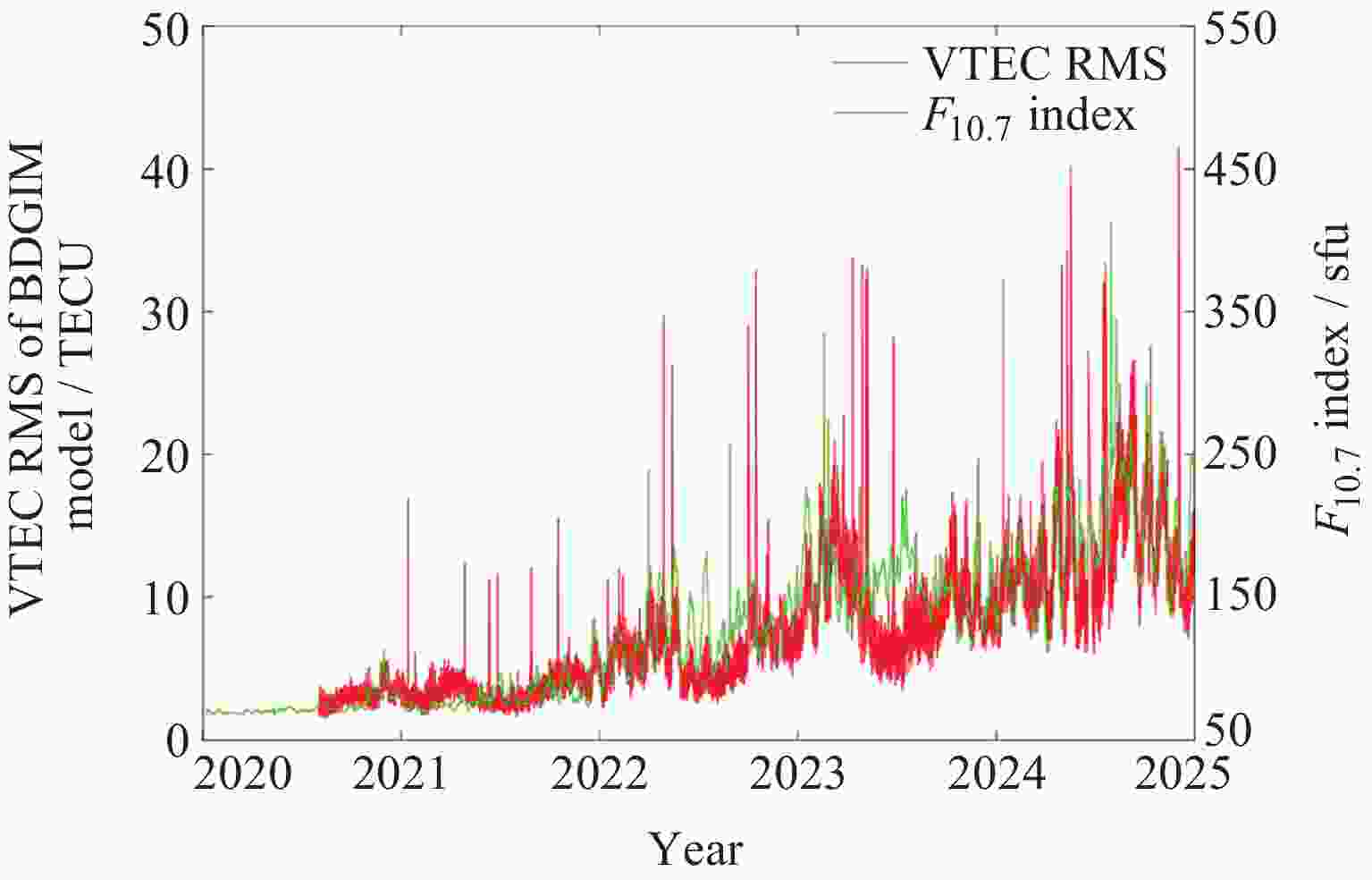
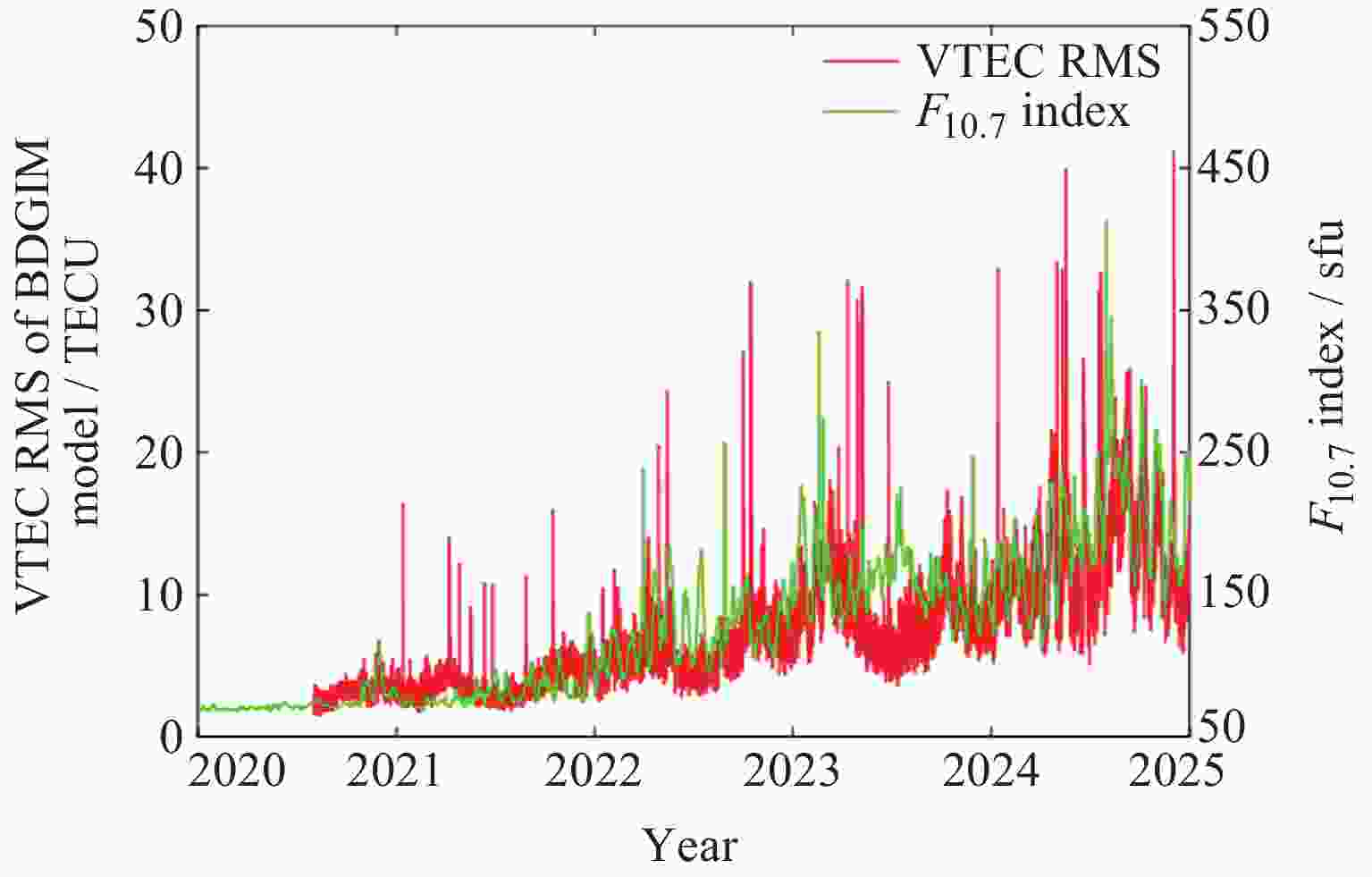
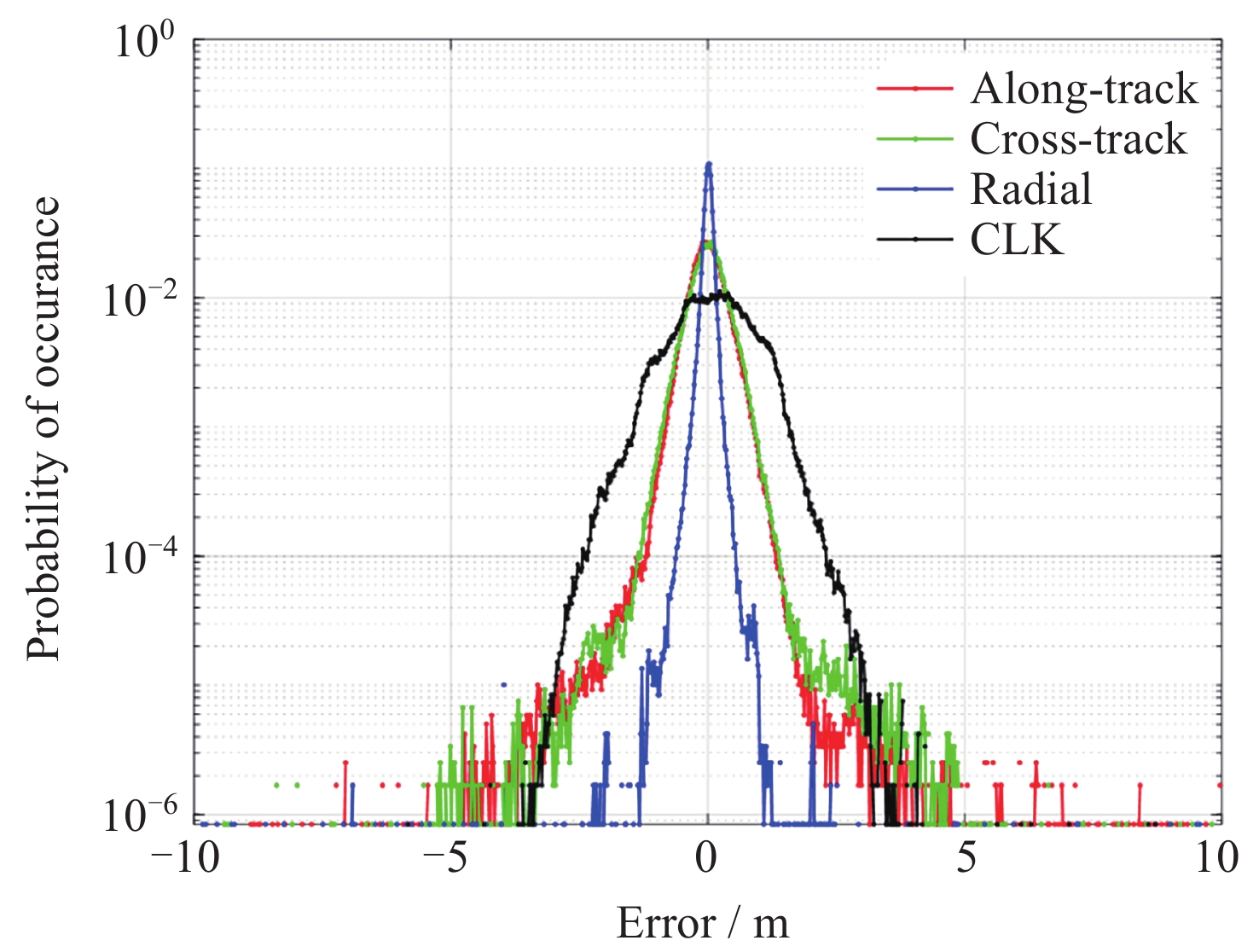
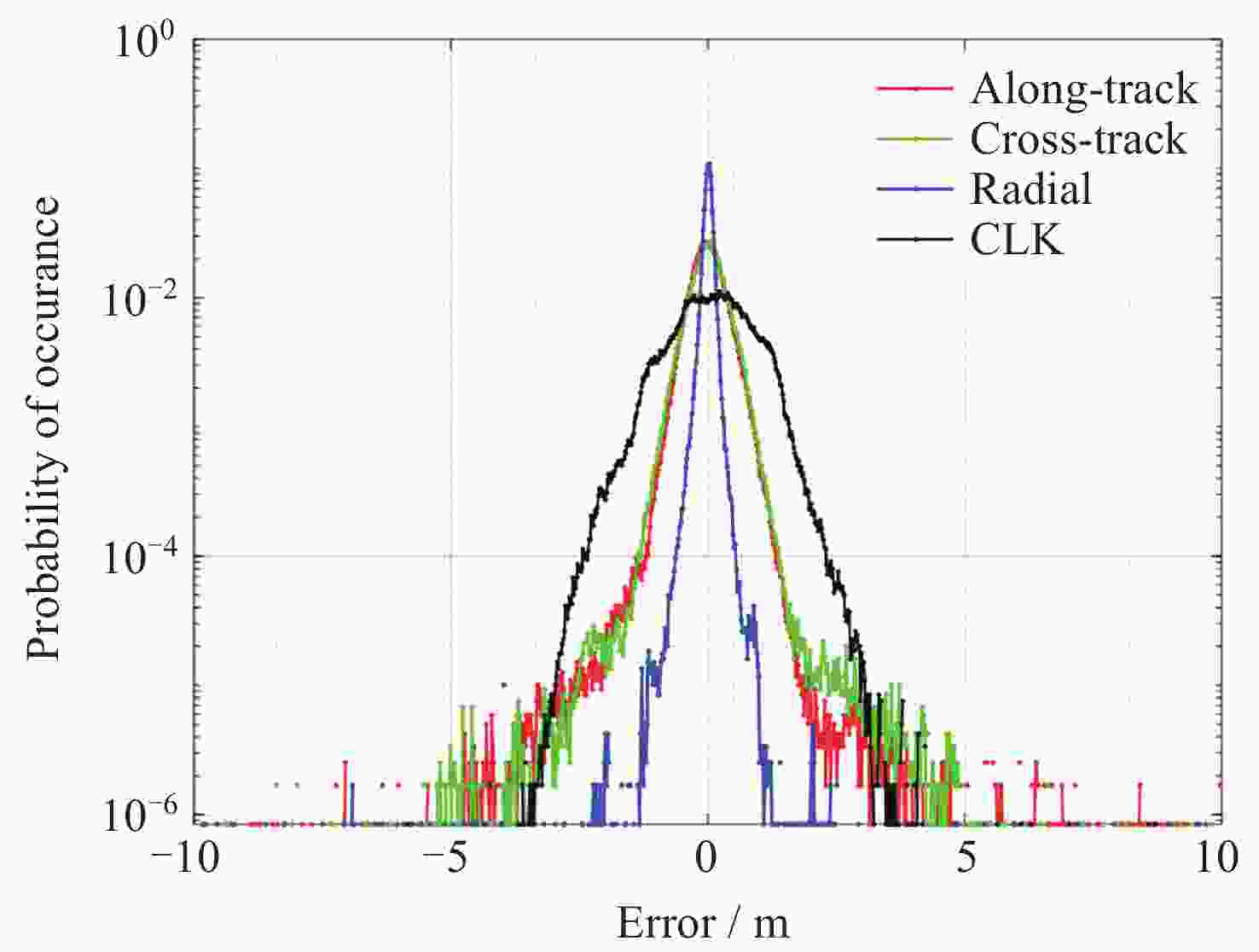
摘要: 北斗三号全球卫星导航系统(BDS-3)于2020年7月31日正式开通, 其空间段服务能力是决定系统整体性能表现的重要因素. 本文对广播轨道、广播钟差、空间信号测距误差、广播电离层精度的评估计算方法进行了分析, 分别以GFZ (German Research Centre for Geosciences)和iGMAS (International GNSS Monitoring and Assessment System)的最终产品为参考基准, 对系统从2020年正式开通至2025年的变化情况进行了评估分析. 研究表明, BDS-3广播轨道精度呈现明显的卫星类型相关性, MEO卫星高于IGSO卫星, 与GFZ产品和iGMAS产品相比, 径向、切向、法向 95% 的 RMS值均得到不同程度地改善; 广播钟差误差与SISRE (Signal-In-Space Range Error) 95%的 RMS值则提升了分米级的精度; 电离层模型误差方面, 在评估周期内, Klobuchar模型的VTEC值分布范围相对较广, 低VTEC区间BDGIM模型的频次分布更为集中; 与CODE和iGMAS电离层产品相比, 在太阳活动极小期的2020年BDGIM (Beidou Global Lonospheric Delay Correction Model) 模型VTEC平均RMS值优于Klobuchar模型, 而在太阳活动极大期的2025年两模型的VTEC平均RMS值均呈上升的趋势, 且BDGIM模型的稳定性更强.Abstract: The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3) officially began providing global services on 31 July 2020. As the core component of satellite navigation systems, the space segment’s service capability determines the overall system performance. This paper first introduces calculation and analysis methods for broadcast orbit errors, broadcast clock errors, Signal-in-space range error and broadcast ionospheric errors. Then, based on the final products of German Geosciences Research Centre (GFZ) and International Global Navigation Satellite System Monitoring and Assessment System (iGMAS), it conducts an evaluation of the changes in broadcast ephemeris accuracy and ionospheric model precision throughout a complete cycle from 2020 to 2025. Research shows that the BDS-3 broadcast orbit error shows a clear dependence on satellite type, with MEO satellites outperforming IGSO satellites. Compared with GFZ products, the 95% RMS of the radial, along-track and cross-track error falls from 0.104, 0.482, 0.589 m respectively in 2020 to 0.080, 0.351, 0.364 m respectively in 2025; and compared with iGMAS products, these data fall from 0.086, 0.386, 0.461 m respectively in 2020 to 0.073 m, 0.341 m, 0.350 m in 2025. Regarding broadcast clock error, based on GFZ products, the 95% RMS improves from 0.705 m in 2020 to 0.540 m in 2025; and based on iGMAS products, the 95% RMS in 2020 is 0.811 m and 0.640 m in 2025. The SISRE of MEO satellites is generally smaller than that of IGSO satellites, and the statistical accuracies of 95% RMS of SISRE in 2020 based on GFZ and iGMAS products reaches 0.705 m and 0.817 m, and in 2025 reaches 0.549 m and 0.645 m, respectively. In terms of ionospheric model errors, throughout the evaluation period, the Klobuchar model exhibited a relatively broad distribution range of VTEC values. The BDGIM model demonstrated a more concentrated frequency distribution in the low VTEC intervals, while the Klobuchar model showed a relatively dispersed distribution in the high VTEC intervals. Compared with CODE and IGMAS ionospheric products, during the solar minimum period (2020), the BDGIM model achieved average VTEC RMS values of 3.193, 6.240, 1.570 TECU and 3.176, 6.790, 1.480 TECU, respectively, while the Klobuchar model yielded 7.359, 35.440, 4.350 TECU and 7.367, 35.930, 4.140 TECU, respectively. During the solar maximum period (2025), the average VTEC RMS values increased to 11.481 TECU and 10.493 TECU, 22.211 TECU and 21.802 TECU, respectively. Based on CODE products as reference, the maximum and minimum VTEC RMS values for the Klobuchar model and BDGIM model were 34.500, 10.400 TECU and 35.330, 6.640 TECU, respectively. The corresponding data referenced against IGMAS products reached 33.810, 10.000 TECU and 35.950, 5.890 TECU, respectively. And the assessment results can provide support for BDS performance optimization.
-
表 1 轨道数据、钟差数据及电离层数据下载链接
Table 1. Download links for orbit data, clock data and ionosphere data
Type Download links BRDM ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn/pub/gps/data/daily/ GFZ ftp://ftp.gfz-potsdam.de/home/GNSS/products/mgex/ iGMAS http://www.igmas.org/Product/TreePage/tree/cate_id/37.html CODE ftp://ftp.aiub.unibe.ch/CODE/ 表 2 以GFZ产品为基准, BDS-3在2020-2025年的轨道误差、钟差误差、SISRE RMS 95%统计精度
Table 2. BDS-3 orbit error, clock error and SISRE RMS 95% statistical precision based on GFZ products in 2020-2025
Year R/m A/m C/m CLK/m SISRE/m 2020 0.104 0.482 0.589 0.705 0.705 2021 0.096 0.502 0.601 0.572 0.580 2022 0.094 0.614 0.657 0.623 0.636 2023 0.097 0.645 0.631 0.584 0.668 2024 0.087 0.354 0.337 0.530 0.542 2025 0.080 0.351 0.364 0.540 0.549 表 3 以iGMAS产品为基准, BDS-3在2020-2025年的轨道误差、钟差误差、SISRE的RMS 95%统计精度
Table 3. BDS-3 orbit error, clock error and SISRE RMS 95% statistical precision based on iGMAS products in 2020―2025
Year R/m A/m C/m CLK/m SISRE/m 2020 0.086 0.386 0.461 0.811 0.817 2021 0.086 0.456 0.505 0.662 0.666 2022 0.087 0.592 0.649 0.716 0.738 2023 0.086 0.635 0.647 0.846 0.883 2024 0.078 0.354 0.331 0.622 0.625 2025 0.073 0.341 0.350 0.640 0.645 表 4 以CODE产品为基准的2020-2025年BDS Klobuchar和BDGIM模型VTEC平均、最大、最小RMS
Table 4. Mean, max and min RMS of VTEC for BDS Klobuchar and BDGIM models based on CODE products from 2020 to 2025
Year BDS Klobuchar/TECU BDGIM/TECU mean max min mean max min 2020 7.359 35.440 4.350 3.193 6.240 1.570 2021 7.420 34.940 3.690 3.545 16.900 1.660 2022 11.096 36.140 4.350 5.923 32.870 2.290 2023 16.626 40.150 6.420 9.337 33.740 3.520 2024 21.039 41.630 7.940 12.025 41.560 6.050 2025 22.211 34.500 10.400 11.481 35.330 6.640 表 5 以iGMAS产品为基准的2020-2025年BDS Klobuchar和BDGIM模型VTEC平均、最大、最小RMS
Table 5. Mean, max and min RMS of VTEC for BDS Klobuchar and BDGIM models based on iGMAS products from 2020 to 2025
Year BDS Klobuchar/TECU BDGIM/TECU mean max min mean max min 2020 7.367 35.930 4.140 3.176 6.790 1.480 2021 7.615 35.180 4.050 3.734 16.400 1.730 2022 10.951 35.590 4.640 5.956 32.030 2.490 2023 15.962 40.010 5.950 8.549 32.140 3.550 2024 20.759 41.550 8.120 11.257 41.210 5.090 2025 21.802 33.810 10.000 10.493 35.950 5.890 -
[1] 王朝辉, 马下平, 严丽, 等. 北斗三号全球卫星导航系统的广播星历精度评估[J]. 测绘通报, 2021(1): 59-65WANG Zhaohui, MA Xiaping, YAN Li, et al. Accuracy assessment of BDS-3 broadcast ephemeris[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2021(1): 59-65 [2] 全国北斗卫星导航标准化技术委员会. 北斗卫星导航术语: GB/T 39267‒2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020: 3National Beidou Navigation Satellite Standardization Technical Committee of the People’s Republic of China. Terminology for Beidou Navigation Satellite System (BDS): GB/T 39267‒2020[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020: 3 [3] YANG Y X, MAO Y, SUN B J. Basic performance and future developments of Beidou global navigation satellite system[J]. Satellite Navigation, 2020, 1(1): 1 doi: 10.1186/s43020-019-0006-0 [4] 许扬胤, 杨元喜, 曾安敏, 等. 北斗三号全球系统空间信号精度评估分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2020, 40(10): 1000-1006 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2020.10.002XU Yangyin, YANG Yuanxi, ZENG Anmin, et al. Accuracy assessment of signal in space of BDS-3 global system[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2020, 40(10): 1000-1006 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2020.10.002 [5] 刘东亮, 成芳, 沈朋礼, 等. 北斗三号全球卫星导航系统空间信号精度评估[J]. 全球定位系统, 2022, 47(2): 114-125 doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2021112201LIU Dongliang, CHENG Fang, SHEN Pengli, et al. Accu racy assessment of BDS-3 satellite signal-in-space[J]. GNSS World of China, 2022, 47(2): 114-125 doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2021112201 [6] 蔡玉林, 吴汤婷, 范亚楠, 等. 北斗GEO/IGSO/MEO卫星广播星历的轨道精度评估[J]. 江西科学, 2024, 42(5): 1027-1033 doi: 10.13990/j.issn1001-3679.2024.05.018CAI Yulin, WU Tangting, FAN Yanan, et al. Evaluation of orbital accuracy for BDS GEO/IGSO/MEO satellite broadcast ephemeris[J]. Jiangxi Science, 2024, 42(5): 1027-1033 doi: 10.13990/j.issn1001-3679.2024.05.018 [7] 鲍任杰, 唐成盼, 胡小工, 等. 北斗广播电离层模型精度评估研究[J/OL]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023: 1-14[2023-12-07]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2023.0588BAO Renjie, TANG Chengpan, HU Xiaogong, et al. Study on the accuracy evaluation of BeiDou broadcast ionospheric model[J/OL]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023: 1-14[2023-12-07]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2023.0588 [8] ZHANG H F, LONG M L, YANG H F, et al. Overview of satellite laser ranging for BeiDou navigation satellite system[J]. Aerospace China, 2020, 21(4): 31-41 [9] 中国卫星导航系统管理办公室. 北斗卫星导航系统空间信号接口控制文件公开服务信号B1I(3.0版)[EB/OL]. (2019-02-27)[2019-12-20]. http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201902/P020190227593621142475.pdfChina Satellite Navigation Office (CSNO). BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal In Space Interface Control Document Open Service Signal B1I(version 3.0)[EB/OL]. (2019-02-27)[2019-12-20]. http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201902/P020190227593621142475.pdf [10] 郭树人, 蔡洪亮, 孟轶男, 等. 北斗三号导航定位技术体制与服务性能[J]. 测绘学报, 2019, 48(7): 810-821GUO Shuren, CAI Hongliang, MENG Yinan, et al. BDS-3 RNSS technical characteristics and service performance[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(7): 810-821 [11] 姚文豪. 北斗三号卫星多频差分码偏差估计与电离层预报[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2022YAO Wenhao. Estimation of Multi-Frequency Differential Code Bias of Beidou-3 Satellite and Ionospheric Forecast[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2022 [12] 刘路, 郭金运, 周茂盛, 等. GNSS广播星历轨道和钟差精度分析[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2022, 47(7): 1122-1132 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200166LIU Lu, GUO Jinyun, ZHOU Maosheng, et al. Accuracy analysis of GNSS broadcast ephemeris orbit and clock offset[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(7): 1122-1132 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200166 [13] 张柔. 北斗/GNSS空间信号精度评估方法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2019ZHANG Rou. Research on BDS/GNSS Signal-in-Space User Range Evaluation Method[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2019 [14] 王海春. GNSS空间信号精度评估分析[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020. DOI: 10.26976/d.cnki.gchau.2020.002089WANG Haichun. Accuracy Assessment and Analysis of GNSS Signal in Space[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2020. DOI: 10.26976/d.cnki.gchau.2020.002089 [15] 张柔, 胡志刚, 陶钧, 等. 顾及不同天线相位中心改正模型的北斗空间信号精度评估方法[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2019, 44(6): 806-813 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180388ZHANG Rou, HU Zhigang, TAO Jun, et al. BDS signal-in-space user range error evaluation considering different antenna phase center offset models[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(6): 806-813 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180388 [16] MONTENBRUCK O, STEIGENBERGER P, HAUSCHILD A. Broadcast versus precise ephemerides: a multi-GNSS perspective[J]. GPS Solutions, 2015, 19(2): 321-333 doi: 10.1007/s10291-014-0390-8 [17] 景鑫, 车通宇, 周舒涵, 等. 北斗三号系统开通前后广播星历精度对比分析[J]. 全球定位系统, 2022, 47(4): 23-30 doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2022051JING Xin, CHE Tongyu, ZHOU Shuhan, et al. Comparative analysis of broadcast ephemeris accuracy before and after the opening of BDS-3 system[J]. GNSS World of China, 2022, 47(4): 23-30 doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2022051 [18] 韩喜豪, 郑帅勇, 杨建雷, 等. 卫星导航中电离层误差校正技术现状与发展[J]. 全球定位系统, 2024, 49(2): 111-126 doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2023105HAN Xihao, ZHENG Shuaiyong, YANG Jianlei, et al. Status and development of the ionospheric error correction techniques in satellite navigation[J]. GNSS World of China, 2024, 49(2): 111-126 doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2023105 [19] 许龙霞, 李孝辉, 何雷. 北斗三号电离层模型性能分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 341-348 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.03.341XU Longxia, LI Xiaohui, HE Lei. Performance analysis of BDS single frequency ionosphere model[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(3): 341-348 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.03.341 [20] 郭睿, 黄张裕, 孙瑞, 等. 北斗三号BDGIM模型的适用性分析[J]. 海洋测绘, 2021, 41(4): 61-64,73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2021.04.013GUO Rui, HUANG Zhangyu, SUN Rui, et al. Applicability analysis of BDGIM model of BDS-3 system[J]. Hydrographic Surveying And Charting, 2021, 41(4): 61-64,73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2021.04.013 [21] 冯来平, 毛悦, 宋小勇, 等. 低轨卫星与星间链路增强的北斗卫星联合定轨精度分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(S2): 109-115 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.F032FENG Laiping, MAO Yue, SONG Xiaoyong, et al. Analysis of the accuracy of Beidou combined orbit determination enhanced by LEO and ISL[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(S2): 109-115 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.F032 [22] 毛悦, 宋小勇, 张清华, 等. BDS-3卫星钟在轨性能评估与分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2023, 52(3): 349-356MAO Yue, SONG Xiaoyong, ZHANG Qinghua, et al. Performance evaluation and comparison of on-orbit satellite clocks for BDS-3[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2023, 52(3): 349-356 [23] 钱文进, 张琳, 安丽超, 等. 北斗三号广播星历空间信号测距误差分析[J]. 地理信息世界, 2022, 29(3): 86-90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2022.03.016QIAN Wenjin, ZHANG Lin, AN Lichao, et al. Analysis of signal-in-space range error for BDS-3 broadcast ephemeris[J]. Geomatics World, 2022, 29(3): 86-90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2022.03.016 [24] YANG C, GUO J, GENG T, et al. Assessment and comparison of broadcast ionospheric models: NTCM-BC, BDGIM, and Klobuchar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(7): 1215 doi: 10.3390/rs12071215 [25] 李涌涛, 李建文, 代桃高, 等. 太阳活动对电离层TEC变化影响分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(6): 847-854 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.06.847LI Yongtao, LI Jianwen, DAI Taogao, et al. Influence of solar activity on ionospheric TEC change[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(6): 847-854 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.06.847 [26] 丁毅涛, 郭美军, 范顺西, 等. 广播电离层模型精度评估分析[J]. 导航定位学报, 2022, 10(1): 53-63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2022.01.008DING Yitao, GUO Meijun, FAN Shunxi, et al. Accuracy evaluation of broadcast ionosphere model[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2022, 10(1): 53-63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2022.01.008 [27] 朱永兴, 谭述森, 任夏, 等. GNSS全球广播电离层模型精度分析[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2020, 45(5): 768-775 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180439ZHU Yongxing, TAN Shusen, REN Xia, et al. Accuracy analysis of GNSS global broadcast ionospheric model[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(5): 768-775 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180439 -
-




 郝鑫宇 男, 2001年2月出生于河北省遵化市, 现为中国电子科技集团公司第十五研究所硕士研究生. E-mail:
郝鑫宇 男, 2001年2月出生于河北省遵化市, 现为中国电子科技集团公司第十五研究所硕士研究生. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: