Shape and Sooting Characteristics of Methane Laminar-jet Diffusion Flames in Microgravity
-
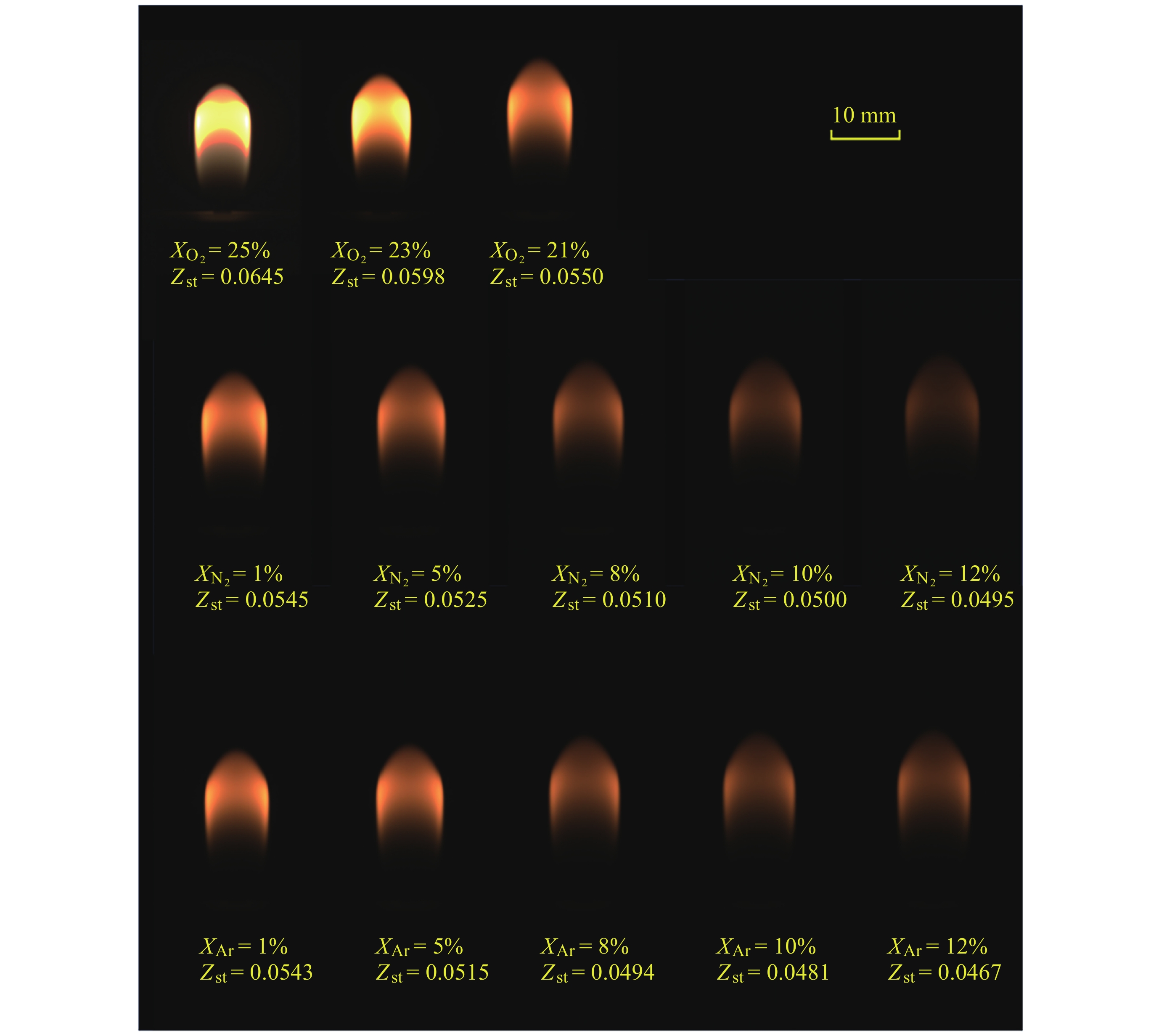
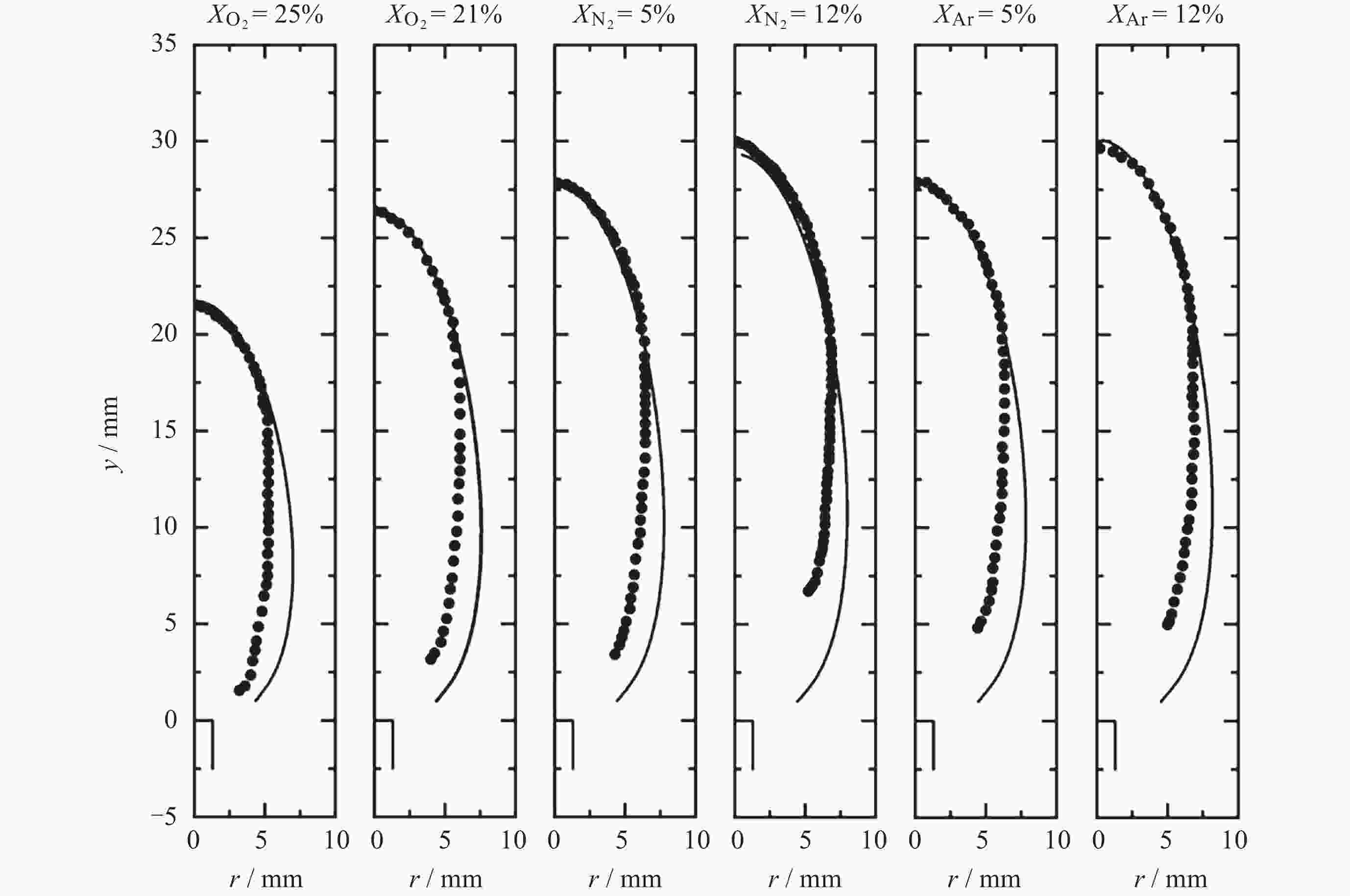
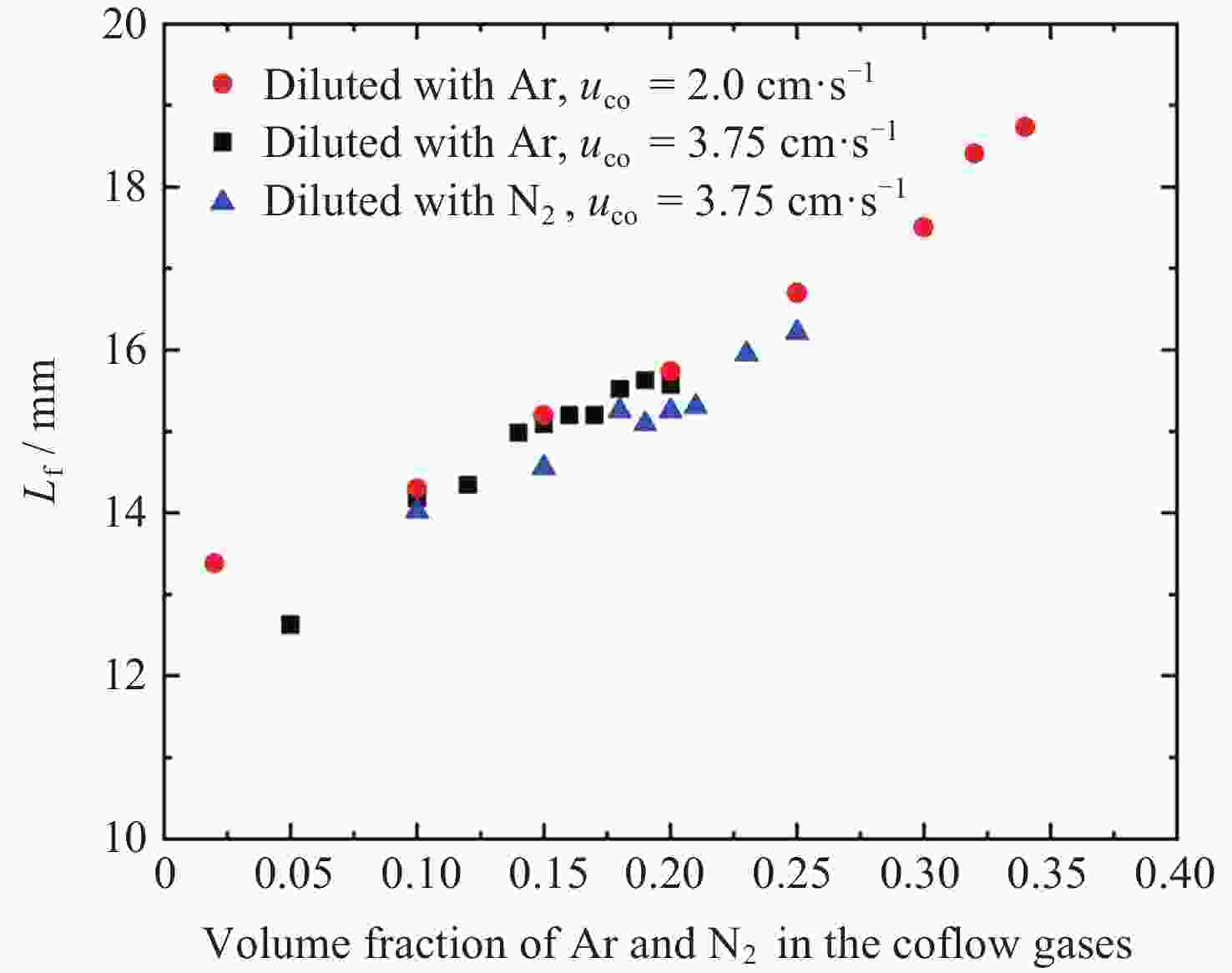
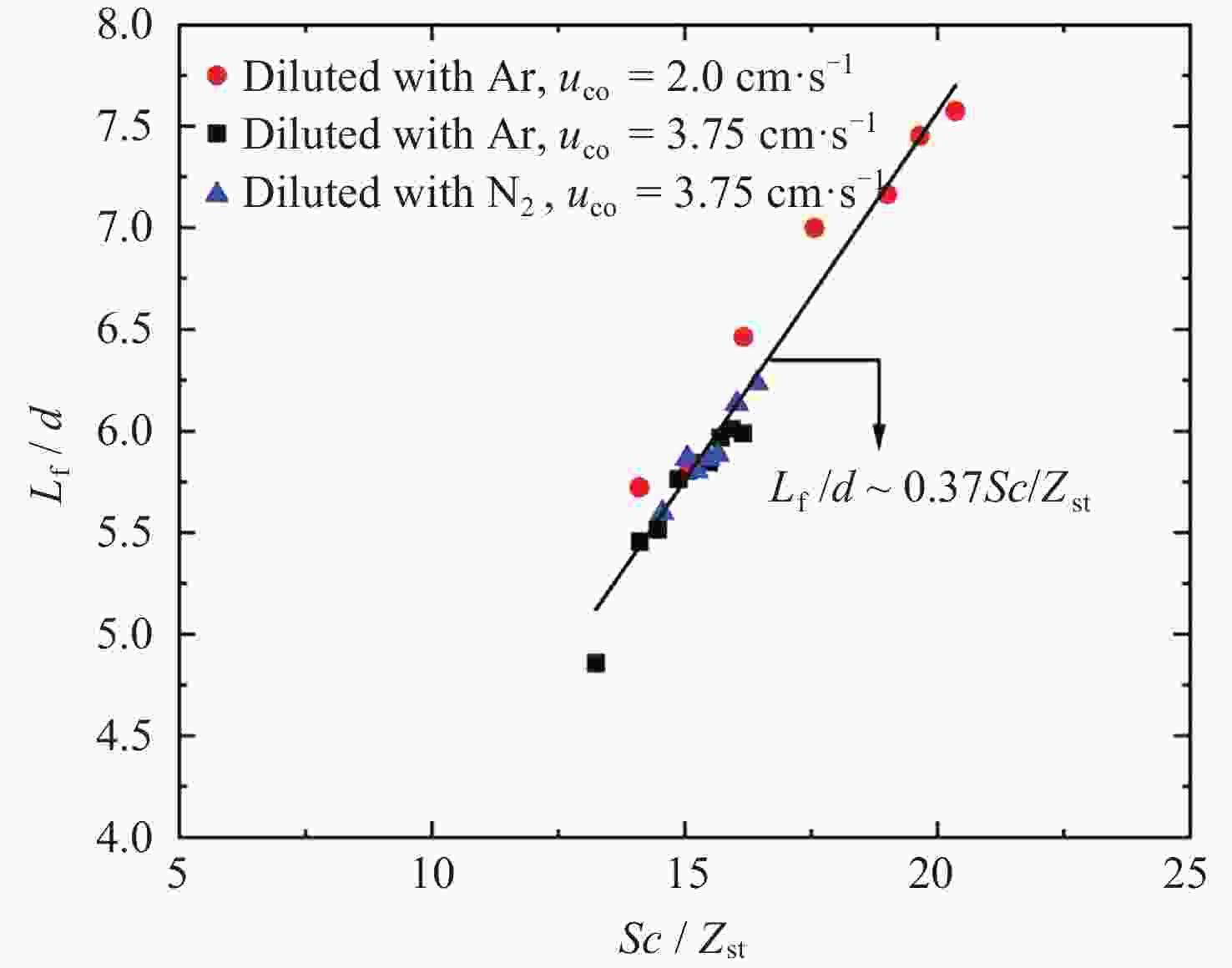
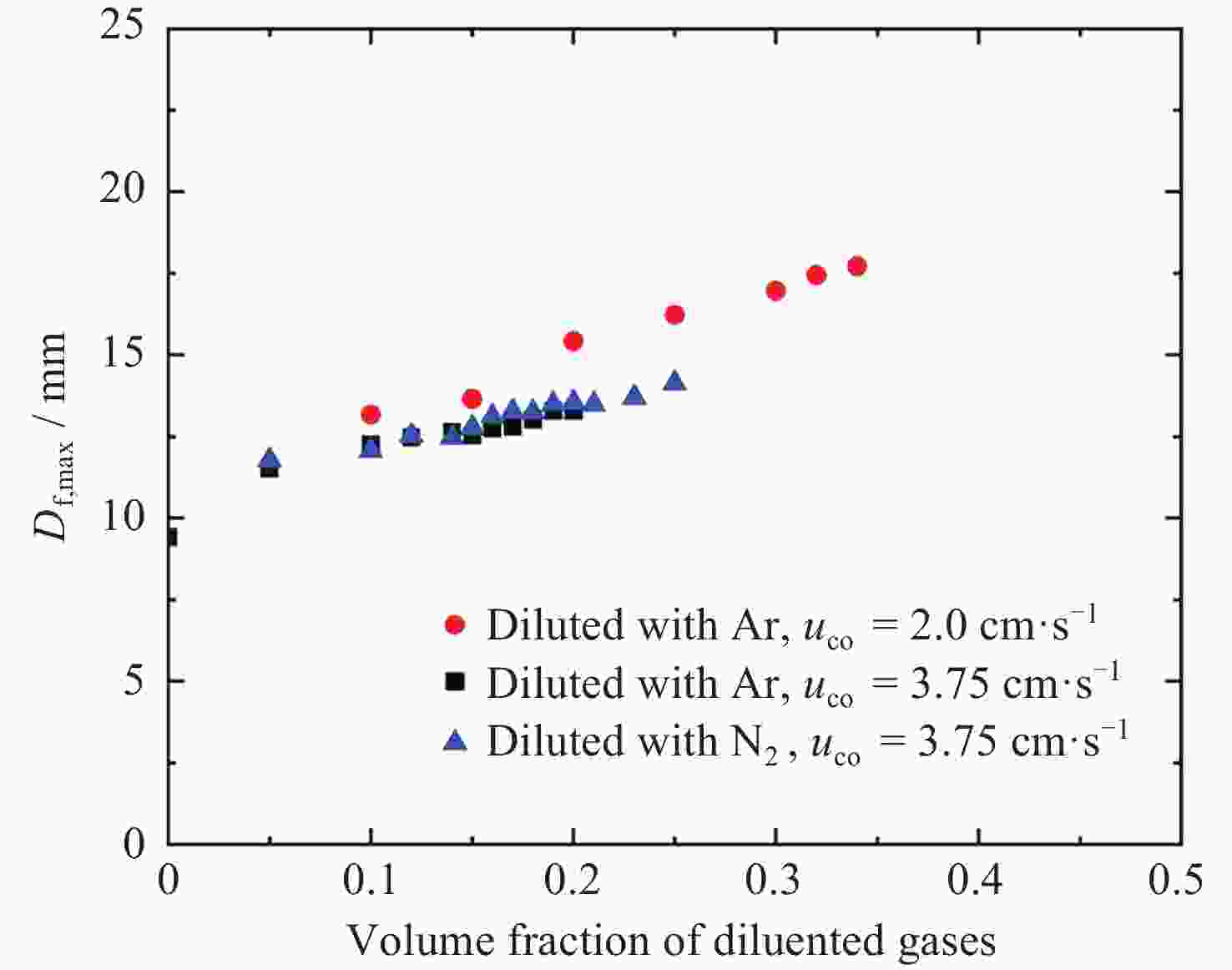
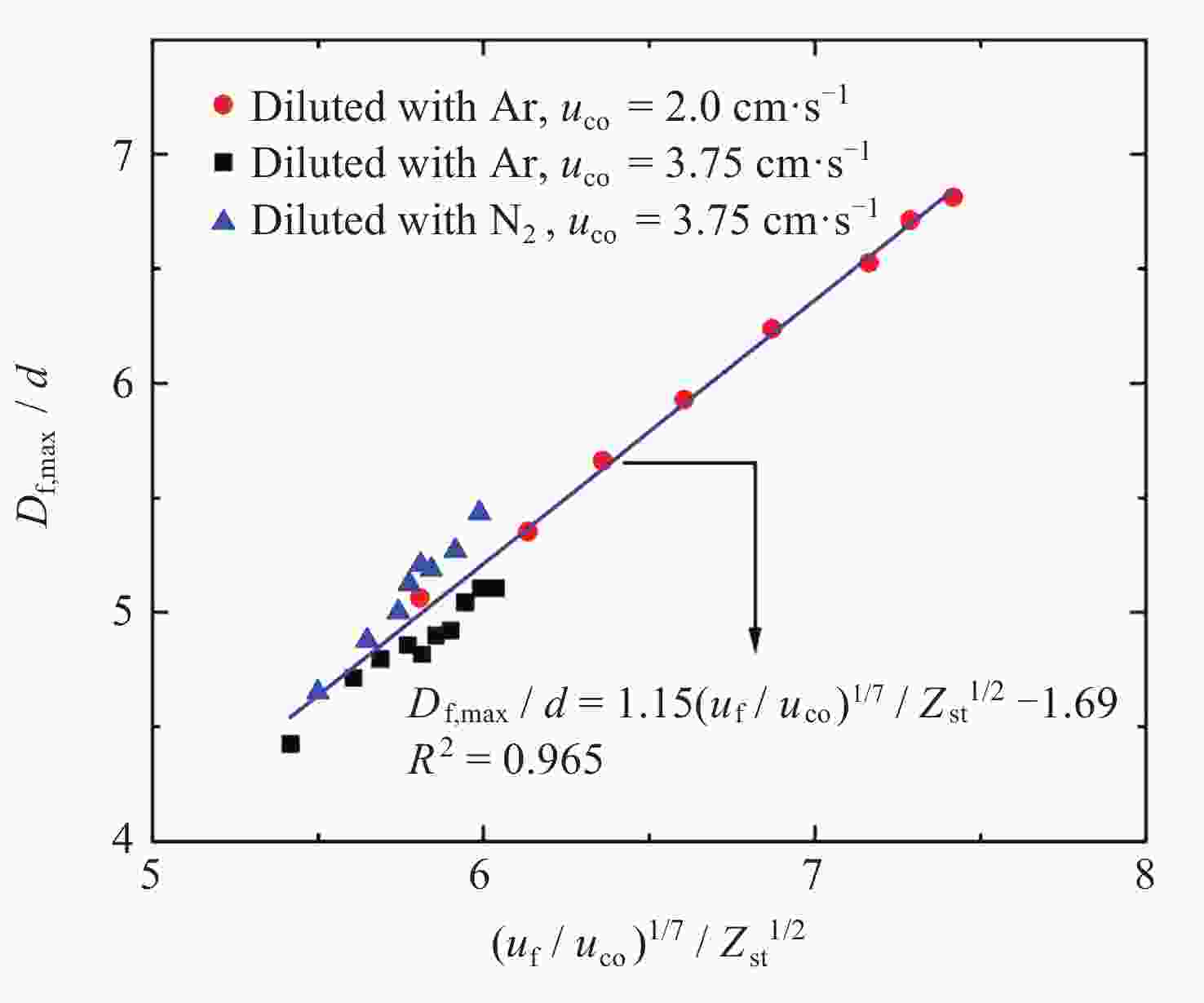
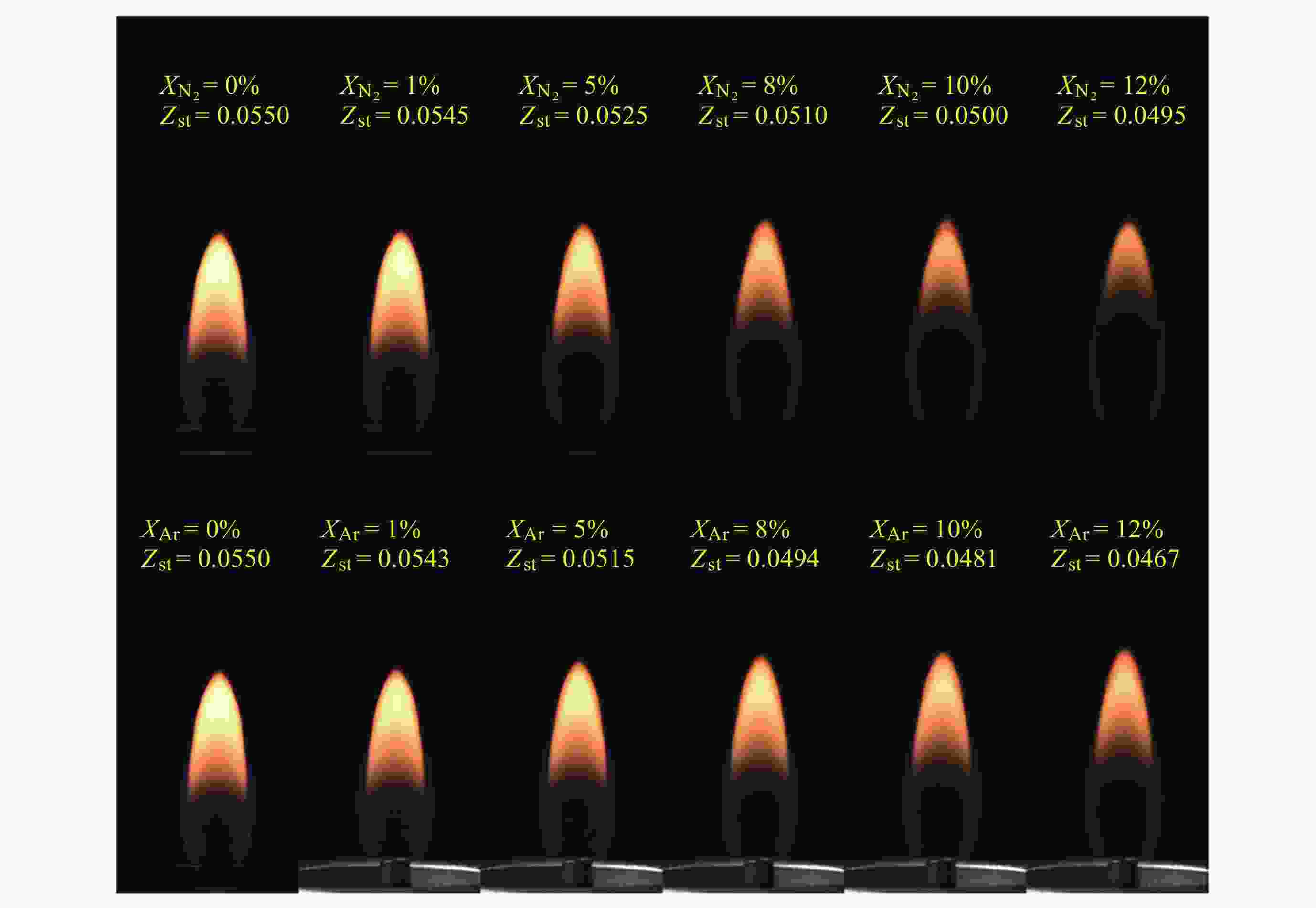
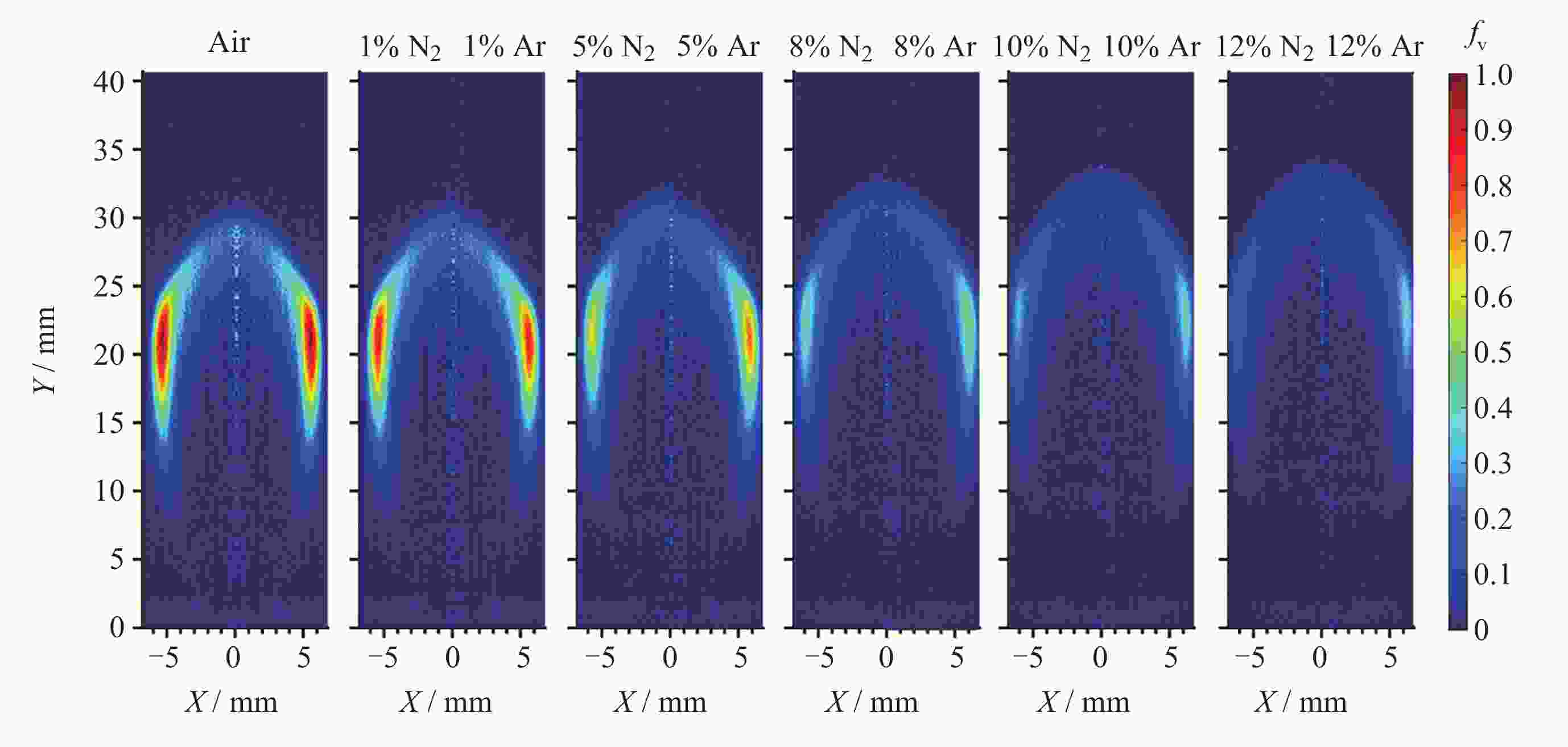
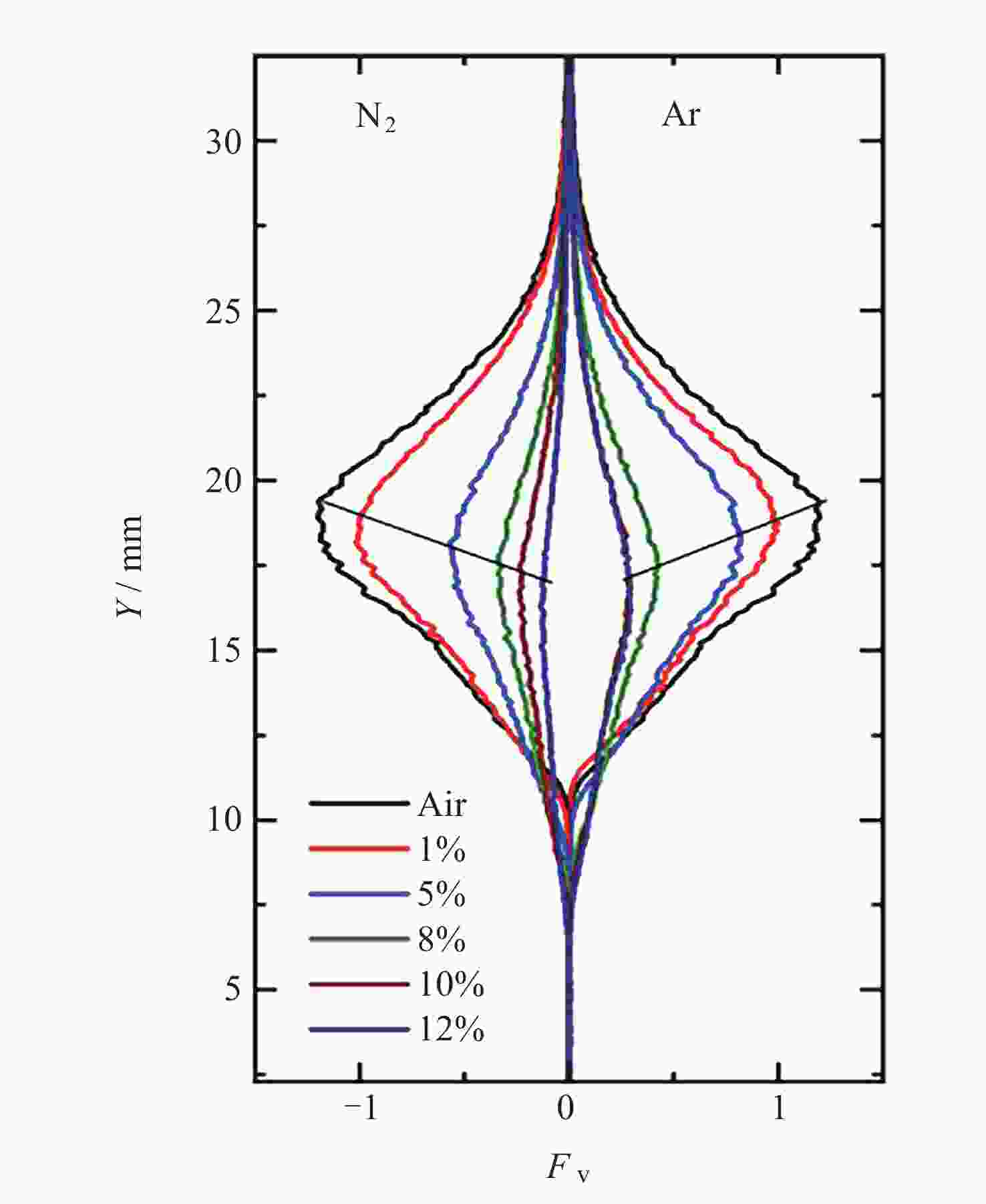
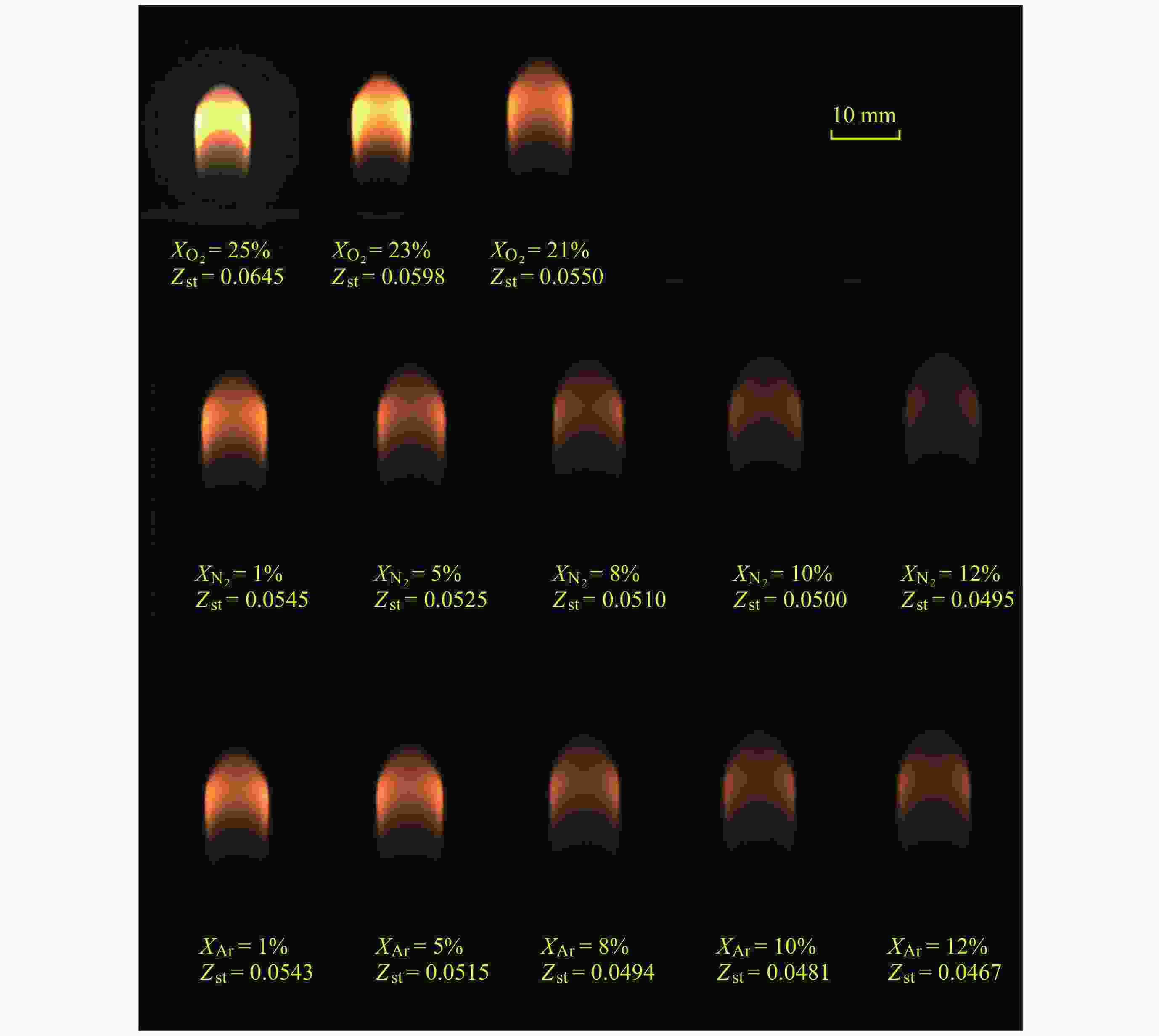
摘要: 几何形态与碳烟特征是碳氢燃料扩散火焰的基本特性. 微重力下层流扩散火焰特性研究可为揭示扩散燃烧的物理和化学机理以及建立湍流扩散燃烧模型提供重要途径. 本研究利用中国空间站中的燃烧科学实验柜对同轴伴流甲烷层流射流扩散火焰进行了在轨微重力实验, 着重分析伴流条件对微重力火焰形态特征和碳烟特性的影响规律. 实验在常温常压环境下进行, 伴流包含不同氧气浓度的氮氧混合气体以及不同N2和Ar稀释比例的空气, 伴流速度/射流速度比值小于0.5, 产生远场和近场射流火焰的甲烷流量. 研究结果表明, 基于射流流场相似理论的简化模型能够对射流远场中微重力火焰的形状进行有效预测, 伴流组分通过改变燃烧化学计量关系影响火焰形状; 近场火焰长度与伴流速度无关, 与化学当量混合分数Zst成反比, 火焰最大直径与Zst倒数的平方根成正比. 用惰性气体稀释伴流空气时, 射流扩散火焰中以碳烟生成反应为主要过程的区域减小、以碳烟氧化反应为主要过程的区域增大, 随着稀释程度的增加, 火焰内的碳烟含量随之减少, 稀释效应和热效应对碳烟生成的影响分别由惰性气体体积分数和火焰温度表征.Abstract: Geometric morphology and soot characteristics are fundamental properties of hydrocarbon fuel diffusion flames. Investigating laminar diffusion flame behavior under microgravity conditions provides a crucial approach for elucidating the physical and chemical mechanisms of diffusion combustion and for establishing turbulent diffusion combustion models. On-orbit microgravity experiments were conducted on coaxial co-flow methane laminar jet diffusion flames using the combustion science experiment cabinet aboard the Chinese Space Station. The study focused on analyzing the influence of co-flowing gases on morphological characteristics and soot properties of microgravity flames. Experiments were conducted under ambient temperature and pressure conditions. The co-flowing gases comprised nitrogen-oxygen mixtures with varying oxygen concentrations and air diluted with different ratios of N2 and Ar. The ratio of entrainment velocity to jet velocity was maintained below 0.5, with methane flow rates generating both far-field and near-field jet flames. Results indicate that a simplified model based on jet flow field similarity theory can effectively predict the shape of microgravity flames in the far-field region of the jet. Co-flow composition affects the flame shape by altering the combustion stoichiometry. Near-field flame length is independent of the co-flowing velocity but inversely proportional to the stoichiometric mixture fraction Zst, while the maximum flame diameter is proportional to the square root of the inverse of Zst. When diluting the co-flowing air with an inert gas, the region dominated by soot formation in the jet diffusion flame decreases, while the region dominated by soot oxidation increases. As dilution increases, the soot content within the flame decreases. The effects of dilution and thermal effects on soot formation are characterized by the volume fraction of the inert gas and the flame temperature, respectively. Diffusion flames in microgravity provide an ideal research subject for understanding fundamental combustion processes and mechanisms. The findings of this study offer foundational data for elucidating basic combustion phenomena and advancing combustion theory, holding significant importance.
-
Key words:
- Laminar diffusion flame /
- Jet /
- Co-flow /
- Methane /
- Microgravity /
- China Space Station (CSS)
-
表 1 微重力实验中甲烷射流和伴流条件的设定
Table 1. Settings of methane jet and coflow conditions in microgravity experiments
甲烷流量/(L·min–1) 伴流速度uco/(cm·s–1) 伴流气体组分 0.12 7.5 O2/N2: O2体积分数 ($ {X}_{{{\text{O}}_{2}}} $) 25%, 23%, 21% (Air)
Air/N2: N2体积分数 ($ {X}_{{{\mathrm{N}}_{2}}} $) 0.01~0.12
Air/Ar: Ar体积分数 ($ {X}_{\text{Ar}} $) 0.01~0.120.05 3.75 Air/N2: N2体积分数 ($ {X}_{{{\mathrm{N}}_{2}}} $) 0.05~0.25
Air/Ar: Ar体积分数 ($ {X}_{\text{Ar}} $) 0.05~0.200.05 2.0 Air/Ar: Ar体积分数 ($ {X}_{\text{Ar}} $) 0.02~0.34 -
[1] WILLIAMS F A. Progress in knowledge of flamelet structure and extinction[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2000, 26(4/5/6): 657-682 doi: 10.1016/s0360-1285(00)00012-5 [2] SUNDERLAND P B, FAETH G M. Soot formation in hydrocarbon/air laminar jet diffusion flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 1996, 105(1-2): 132-146 doi: 10.1016/0010-2180(95)00182-4 [3] URBAN D L, YUAN Z G, SUNDERLAND P B, et al. Structure and soot properties of nonbuoyant ethylene/air laminar jet diffusion flames[J]. AIAA Journal, 1998, 36(8): 1346-1360 doi: 10.2514/2.542 [4] URBAN D L, YUAN Z G, SUNDERLAND P B, et al. Smoke-point properties of non-buoyant round laminar jet diffusion flames[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2000, 28(2): 1965-1972 doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(00)80602-5 [5] JALAIN R, BONNETY J, MATYNIA A, et al. Influence of sub-atmospheric pressure on flame shape and sooting propensity in ethylene laminar coflow non-premixed flame[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2024, 259: 113173 doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2023.113173 [6] SPALDING D B. Combustion and Mass Transfer: A Textbook with Multiple-Choice Exercises for Engineering Students[M]. Oxford: Pergamon, 1979: 185-195 [7] LIN K C, FAETH G M. Shapes of nonbuoyant round luminous laminar-jet diffusion flames in coflowing air[J]. AIAA Journal, 1999, 37(6): 759-765 doi: 10.2514/2.785 [8] LIN K C, FAETH G M, SUNDERLAND P B, et al. Shapes of nonbuoyant round luminous hydrocarbon/air laminar jet diffusion flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 1999, 116(3): 415-431 doi: 10.1016/s0010-2180(98)00100-x [9] WALSH K T, FIELDING J, SMOOKE M D, et al. Experimental and computational study of temperature, species, and soot in buoyant and non-buoyant coflow laminar diffusion flames[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2000, 28(2): 1973-1979 doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(00)80603-7 [10] DIEZ F J, AALBURG C, SUNDERLAND P B, et al. Soot properties of laminar jet diffusion flames in microgravity[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2009, 156(8): 1514-1524 [11] JEON B H, CHOI J H. Effect of buoyancy on soot formation in gas-jet diffusion flame[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2010, 24(7): 1537-1543 doi: 10.1007/s12206-010-0406-4 [12] REIMANN J, KUHLMANN S A, WILL S. Investigations on soot formation in heptane jet diffusion flames by optical techniques[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2010, 22(4): 499-505 doi: 10.1007/s12217-010-9204-y [13] MA B, CAO S, GIASSI D, et al. An experimental and computational study of soot formation in a coflow jet flame under microgravity and normal gravity[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2015, 35(1): 839-846 doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2014.05.064 [14] DOTSON K T, SUNDERLAND P B, YUAN Z G, et al. Laminar smoke points of coflowing flames in microgravity[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2011, 46(8): 550-555 doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2011.08.002 [15] KALVAKALA K C, KATTA V R, AGGARWAL S K. Effects of oxygen-enrichment and fuel unsaturation on soot and NOx emissions in ethylene, propane, and propene flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2018, 187: 217-229 doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2017.09.015 [16] 张振忠, 孔文俊, 张华良. 空间站燃烧科学实验系统设计[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(1): 72-78 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.01.072ZHANG Zhenzhong, KONG Wenjun, ZHANG Hualiang. Design of combustion science experimental system for China space station[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(1): 72-78 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.01.072 [17] 张晓武, 郑会龙, 王琨, 等. 中国空间站燃烧科学实验系统燃烧室设计与分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(2): 301-309ZHANG Xiaowu, ZHENG Huilong, WANG Kun, et al. Combustion chamber design and analysis of the space station combustion science experimental system[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(2): 301-309 [18] WEN Y Z, LI L F, LI X X, et al. Extinction of microgravity partially premixed flame aboard the Chinese space station[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2024, 40(1-4): 105574 doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2024.105574 [19] ZHAO P P, ZHANG X W, FANG Y, et al. On-orbit functional verification of combustion science experimental system in China Space Station[J]. Aerospace, 2025, 12(5): 448 doi: 10.3390/aerospace12050448 [20] WALSH K T, FIELDING J, SMOOKE M D, et al. A comparison of computational and experimental lift-off heights of coflow laminar diffusion flames[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2005, 30(1): 357-365 doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2004.08.186 [21] PRABASENA B, RÖDER M, KATHROTIA T, et al. Strain rate and fuel composition dependence of chemiluminescent species profiles in non-premixed counterflow flames: comparison with model results[J]. Applied Physics B, 2012, 107(3): 561-569 doi: 10.1007/s00340-012-4989-6 [22] 张婷, 郭庆华, 龚岩, 等. CH4/O2同轴射流扩散火焰辐射发光特性[J]. 燃烧科学与技术, 2012, 18(4): 353-358ZHANG Ting, GUO Qinghua, GONG Yan, et al. Luminescent properties of CH4/O2 co-flowing jet diffusion flame[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2012, 18(4): 353-358 [23] KENT J H, HONNERY D R. Soot mass growth in laminar diffusion flames—parametric modelling[M]//BOCKHORN H. Soot Formation in Combustion: Mechanisms and Models. Berlin: Springer, 1994: 199-220 [24] LAUTENBERGER C W, DE RIS J L, DEMBSEY N A, et al. A simplified model for soot formation and oxidation in CFD simulation of non-premixed hydrocarbon flames[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2005, 40(2): 141-176 doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2004.10.002 [25] DU D X, AXELBAUM R L, LAW C K. The influence of carbon dioxide and oxygen as additives on soot formation in diffusion flames[J]. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1991, 23(1): 1501-1507 doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(06)80419-4 [26] LIU F S, GUO H S, SMALLWOOD G J, et al. The chemical effects of carbon dioxide as an additive in an ethylene diffusion flame: implications for soot and NOx formation[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2001, 125(1-2): 778-787 doi: 10.1016/S0010-2180(00)00241-8 [27] WANG Q, LEGROS G, BONNETY J, et al. Experimental characterization of the different nitrogen dilution effects on soot formation in ethylene diffusion flames[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2017, 36(2): 3227-3235 doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2016.07.063 [28] GÜLDER Ö L, SNELLING D R. Influence of nitrogen dilution and flame temperature on soot formation in diffusion flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 1993, 92(1-2): 115-124 doi: 10.1016/0010-2180(93)90202-E -
-




 朱凤 女, 1988年9月出生于山东省泰安市, 现为中国科学院力学研究所副研究员, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为微重力燃烧. E-mail:
朱凤 女, 1988年9月出生于山东省泰安市, 现为中国科学院力学研究所副研究员, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为微重力燃烧. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: